Page 209 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 209
Data Structure
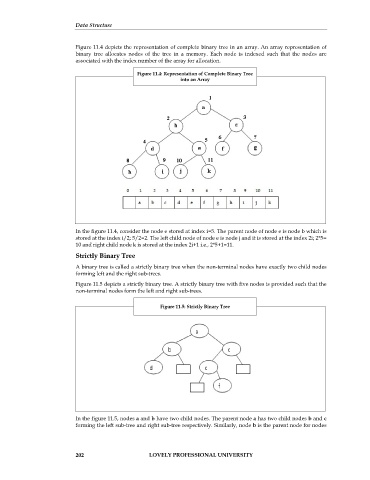
Figure 11.4 depicts the representation of complete binary tree in an array. An array representation of
binary tree allocates nodes of the tree in a memory. Each node is indexed such that the nodes are
associated with the index number of the array for allocation.
Figure 11.4: Representation of Complete Binary Tree
into an Array
In the figure 11.4, consider the node e stored at index i=5. The parent node of node e is node b which is
stored at the index i/2; 5/2=2. The left child node of node e is node j and it is stored at the index 2i; 2*5=
10 and right child node k is stored at the index 2i+1 i.e., 2*5+1=11.
Strictly Binary Tree
A binary tree is called a strictly binary tree when the non-terminal nodes have exactly two child nodes
forming left and the right sub-trees.
Figure 11.5 depicts a strictly binary tree. A strictly binary tree with five nodes is provided such that the
non-terminal nodes form the left and right sub-trees.
Figure 11.5: Strictly Binary Tree
In the figure 11.5, nodes a and b have two child nodes. The parent node a has two child nodes b and c
forming the left sub-tree and right sub-tree respectively. Similarly, node b is the parent node for nodes
202 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY