Page 216 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 216
Unit 11: Introduction to Binary Trees
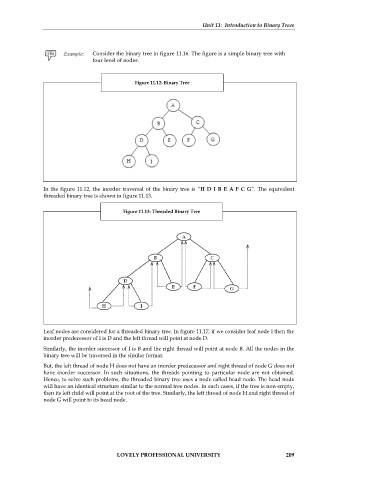
Consider the binary tree in figure 11.16. The figure is a simple binary tree with
four level of nodes.
Figure 11.12: Binary Tree
In the figure 11.12, the inorder traversal of the binary tree is “H D I B E A F C G”. The equivalent
threaded binary tree is shown in figure 11.13.
Figure 11.13: Threaded Binary Tree
Leaf nodes are considered for a threaded binary tree. In figure 11.17, if we consider leaf node I then the
inorder predecessor of I is D and the left thread will point at node D.
Similarly, the inorder successor of I is B and the right thread will point at node B. All the nodes in the
binary tree will be traversed in the similar format.
But, the left thread of node H does not have an inorder predecessor and right thread of node G does not
have inorder successor. In such situations, the threads pointing to particular node are not obtained.
Hence, to solve such problems, the threaded binary tree uses a node called head node. The head node
will have an identical structure similar to the normal tree nodes. In such cases, if the tree is non-empty,
then its left child will point at the root of the tree. Similarly, the left thread of node H and right thread of
node G will point to its head node.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 209