Page 248 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 248
Unit 13: Binary Search Trees
return findMin(node:leftChild)
}
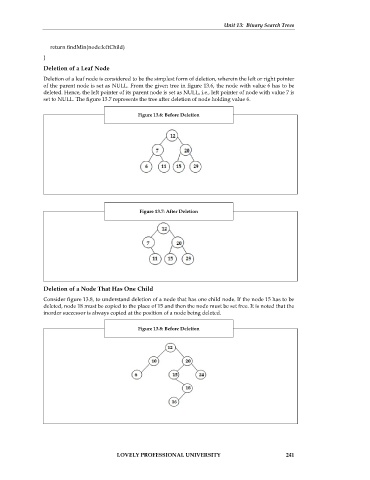
Deletion of a Leaf Node
Deletion of a leaf node is considered to be the simplest form of deletion, wherein the left or right pointer
of the parent node is set as NULL. From the given tree in figure 13.6, the node with value 6 has to be
deleted. Hence, the left pointer of its parent node is set as NULL, i.e., left pointer of node with value 7 is
set to NULL. The figure 13.7 represents the tree after deletion of node holding value 6.
Figure 13.6: Before Deletion
Figure 13.7: After Deletion
Deletion of a Node That Has One Child
Consider figure 13.8, to understand deletion of a node that has one child node. If the node 15 has to be
deleted, node 18 must be copied to the place of 15 and then the node must be set free. It is noted that the
inorder successor is always copied at the position of a node being deleted.
Figure 13.8: Before Deletion
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 241