Page 82 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 82
Unit 4: Pointers
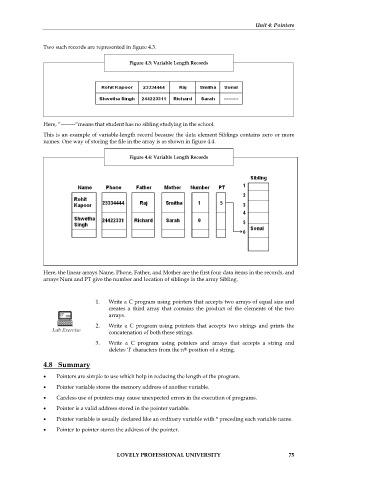
Two such records are represented in figure 4.3.
Figure 4.3: Variable Length Records
Here, “--------“means that student has no sibling studying in the school.
This is an example of variable-length record because the data element Siblings contains zero or more
names. One way of storing the file in the array is as shown in figure 4.4.
Figure 4.4: Variable Length Records
Here, the linear arrays Name, Phone, Father, and Mother are the first four data items in the records, and
arrays Num and PT give the number and location of siblings in the array Sibling.
1. Write a C program using pointers that accepts two arrays of equal size and
creates a third array that contains the product of the elements of the two
arrays.
2. Write a C program using pointers that accepts two strings and prints the
concatenation of both these strings.
3. Write a C program using pointers and arrays that accepts a string and
deletes ‘l’ characters from the n position of a string.
th
4.8 Summary
• Pointers are simple to use which help in reducing the length of the program.
• Pointer variable stores the memory address of another variable.
• Careless use of pointers may cause unexpected errors in the execution of programs.
• Pointer is a valid address stored in the pointer variable.
• Pointer variable is usually declared like an ordinary variable with * preceding each variable name.
• Pointer to pointer stores the address of the pointer.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 75