Page 92 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 92
Unit 5: Introduction to Linked List
printf(“%d\n”, j);
//printf(“%d\n”, n1.next->value); // you can use this statement to print the value
present in node1 or print j directly as depicted in the above statement
printf(“%d/n”, n1.next->value); //Printing the next value of node1
printf(“%d/n”, n2.next->value); //Printing the next value of node2
printf(“%d/n”, n1.previous->value); //Printing the previous value of node1
printf(“%d/n”, n2.previous->value); //Printing the previous value of node2
printf(“%d/n”, n3.previous->value); //Printing the previous value of node3
}
Output:
When you run the program, the following output is obtained:
40
60
0
20
40
In this example:
1. First, a structure named list is created. The list contains an integer data
variable named value to store data, a pointer variable named next_element
to point to next node and a pointer variable named previous_element to
point to previous node.
2. Then, the three objects namely, n1, n2, and n3 are created to access the
structure elements. In the program they act as nodes in a list.
3. In the main() function, the value for nodes n1, n2, and n3 are assigned.
4. Then, the address of n2 is stored in n1 and address of n3 is stored in n2. In
order to traverse backwards, the address of n1 is stored in n2 and address of
n2 is stored in n3. The address of n3 is assigned a NULL value to depict the
end of the list.
5. Finally, the values present in n1, n2, and n3 are printed.
5.3.3 Circular Linked List
In a circular linked list, only one pointer is used to point to another node or next element. It is known as
a circular list because the last node’s pointer points to the HEAD node.
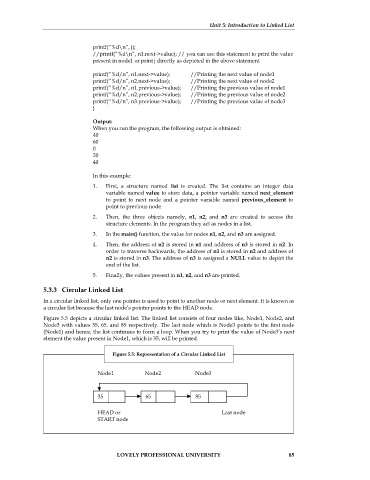
Figure 5.5 depicts a circular linked list. The linked list consists of four nodes like, Node1, Node2, and
Node3 with values 35, 65, and 85 respectively. The last node which is Node3 points to the first node
(Node1) and hence, the list continues to form a loop. When you try to print the value of Node3’s next
element the value present in Node1, which is 35, will be printed.
Figure 5.5: Representation of a Circular Linked List
Node1 Node2 Node3
35 65 85
HEAD or Last node
START node
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 85