Page 18 - SOFTWARE TESTING & QUALITY ASSURANCE
P. 18
Unit 1: Introduction to Software Testing
In XP software development life cycle, programmers usually work in pairs. One programmer takes the
responsibility of writing the code for the software and the other programmer reviews the code to ensure
that it uses simple solutions and follows the best design principles and coding practices. This means the
second programmer acts as a tester and tests the software as and when it is developed to find the bugs.
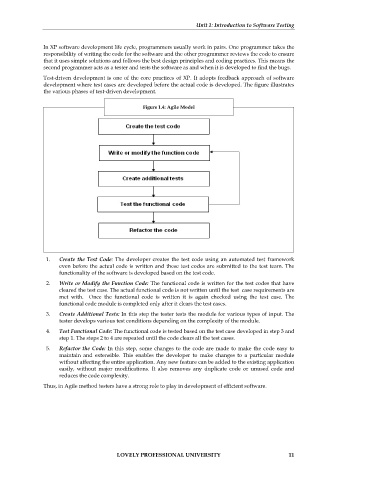
Test-driven development is one of the core practices of XP. It adopts feedback approach of software
development where test cases are developed before the actual code is developed. The figure illustrates
the various phases of test-driven development.
Figure 1.4: Agile Model
1. Create the Test Code: The developer creates the test code using an automated test framework
even before the actual code is written and these test codes are submitted to the test team. The
functionality of the software is developed based on the test code.
2. Write or Modify the Function Code: The functional code is written for the test codes that have
cleared the test case. The actual functional code is not written until the test case requirements are
met with. Once the functional code is written it is again checked using the test case. The
functional code module is completed only after it clears the test cases.
3. Create Additional Tests: In this step the tester tests the module for various types of input. The
tester develops various test conditions depending on the complexity of the module.
4. Test Functional Code: The functional code is tested based on the test case developed in step 3 and
step 1. The steps 2 to 4 are repeated until the code clears all the test cases.
5. Refactor the Code: In this step, some changes to the code are made to make the code easy to
maintain and extensible. This enables the developer to make changes to a particular module
without affecting the entire application. Any new feature can be added to the existing application
easily, without major modifications. It also removes any duplicate code or unused code and
reduces the code complexity.
Thus, in Agile method testers have a strong role to play in development of efficient software.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 11