Page 143 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 143
Computer Graphics
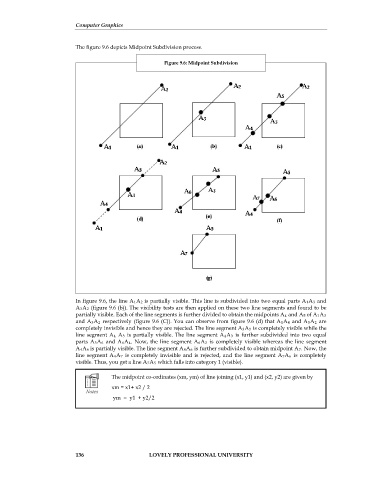
The figure 9.6 depicts Midpoint Subdivision process.
Figure 9.6: Midpoint Subdivision
In figure 9.6, the line A 1A 2 is partially visible. This line is subdivided into two equal parts A 1A 3 and
A 3A 2 (figure 9.6 (b)). The visibility tests are then applied on these two line segments and found to be
partially visible. Each of the line segments is further divided to obtain the midpoints A 4 and A 5 of A 1A 3
and A 3A 2 respectively (figure 9.6 (C)). You can observe from figure 9.6 (d) that A 1A 4 and A 5A 2 are
completely invisible and hence they are rejected. The line segment A 3A 5 is completely visible while the
line segment A 4 A 3 is partially visible. The line segment A 4A 3 is further subdivided into two equal
parts A 3A 6 and A 6A 4. Now, the line segment A 6A 3 is completely visible whereas the line segment
A 4A 6 is partially visible. The line segment A 4A 6 is further subdivided to obtain midpoint A 7. Now, the
line segment A 4A 7 is completely invisible and is rejected, and the line segment A 7A 6 is completely
visible. Thus, you get a line A 7A 5 which falls into category 1 (visible).
The midpoint co-ordinates (xm, ym) of line joining (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are given by
xm = x1+ x2 / 2
ym = y1 + y2/2
136 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY