Page 157 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 157
Computer Graphics
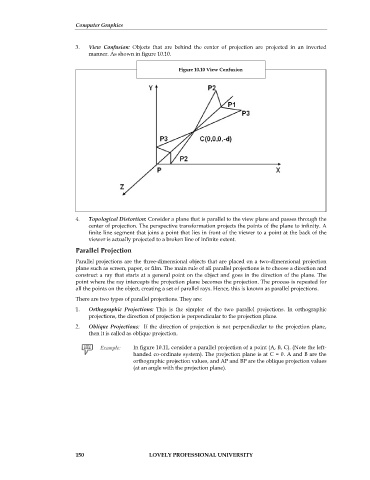
3. View Confusion: Objects that are behind the center of projection are projected in an inverted
manner. As shown in figure 10.10.
Figure 10.10 View Confusion
4. Topological Distortion: Consider a plane that is parallel to the view plane and passes through the
center of projection. The perspective transformation projects the points of the plane to infinity. A
finite line segment that joins a point that lies in front of the viewer to a point at the back of the
viewer is actually projected to a broken line of infinite extent.
Parallel Projection
Parallel projections are the three-dimensional objects that are placed on a two-dimensional projection
plane such as screen, paper, or film. The main rule of all parallel projections is to choose a direction and
construct a ray that starts at a general point on the object and goes in the direction of the plane. The
point where the ray intercepts the projection plane becomes the projection. The process is repeated for
all the points on the object, creating a set of parallel rays. Hence, this is known as parallel projections.
There are two types of parallel projections. They are:
1. Orthographic Projections: This is the simpler of the two parallel projections. In orthographic
projections, the direction of projection is perpendicular to the projection plane.
2. Oblique Projections: If the direction of projection is not perpendicular to the projection plane,
then it is called as oblique projection.
In figure 10.11, consider a parallel projection of a point (A, B, C). (Note the left-
handed co-ordinate system). The projection plane is at C = 0. A and B are the
orthographic projection values, and AP and BP are the oblique projection values
(at an angle with the projection plane).
150 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY