Page 192 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 192
Unit 12: Color and Shading Model
The usage of bilinear interpolation is shown in figure 12.9.
Figure 12.9: Usage of Bilinear Interpolation
Source: Xiang. Z., Plstock. R. (2006). Computer Graphics. 2nd Edition. Tata McGraw Hill. Pg no. 298
A curved surface can be shaded with the help of polygons. The normal vectors at the polygon’s vertices
can be identified in two methods to obtain smooth-looking transition between adjacent polygons. The
first method is to determine the exact surface normal at each vertex location with the help of underlying
curved surface.
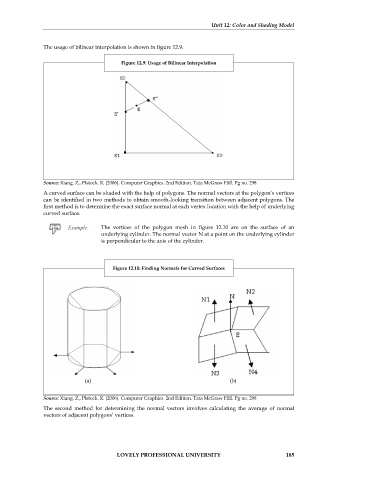
The vertices of the polygon mesh in figure 12.10 are on the surface of an
underlying cylinder. The normal vector N at a point on the underlying cylinder
is perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder.
Figure 12.10: Finding Normals for Curved Surfaces
(a) (b)
Source: Xiang. Z., Plstock. R. (2006). Computer Graphics. 2nd Edition. Tata McGraw Hill. Pg no. 298
The second method for determining the normal vectors involves calculating the average of normal
vectors of adjacent polygons’ vertices.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 185