Page 4 - DCAP506_ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE
P. 4
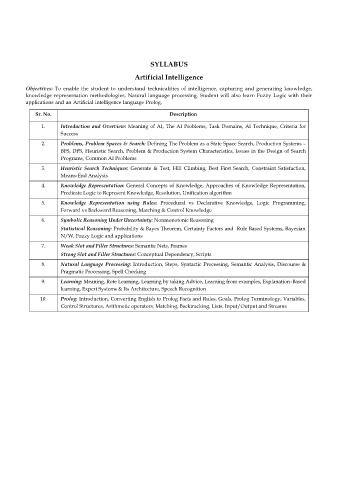
SYLLABUS
Artificial Intelligence
Objectives: To enable the student to understand technicalities of intelligence, capturing and generating knowledge,
knowledge representation methodologies, Natural language processing. Student will also learn Fuzzy Logic with their
applications and an Artificial intelligence language Prolog.
Sr. No. Description
1. Introduction and Overview: Meaning of AI, The AI Problems, Task Domains, AI Technique, Criteria for
Success
2. Problems, Problem Spaces & Search: Defining The Problem as a State Space Search, Production Systems –
BFS, DFS, Heuristic Search, Problem & Production System Characteristics, Issues in the Design of Search
Programs, Common AI Problems
3. Heuristic Search Techniques: Generate & Test, Hill Climbing, Best First Search, Constraint Satisfaction,
Means-End Analysis
4. Knowledge Representation: General Concepts of Knowledge, Approaches of Knowledge Representation,
Predicate Logic to Represent Knowledge, Resolution, Unification algorithm
5. Knowledge Representation using Rules: Procedural vs Declarative Knowledge, Logic Programming,
Forward vs Backward Reasoning, Matching & Control Knowledge
6. Symbolic Reasoning Under Uncertainty: Nonmonotonic Reasoning
Statistical Reasoning: Probability & Bayes Theorem, Certainty Factors and Rule Based Systems, Bayesian
N/W, Fuzzy Logic and applications
7. Weak Slot and Filler Structures: Semantic Nets, Frames
Strong Slot and Filler Structures: Conceptual Dependency, Scripts
8. Natural Language Processing: Introduction, Steps, Syntactic Processing, Semantic Analysis, Discourse &
Pragmatic Processing, Spell Checking
9. Learning: Meaning, Rote Learning, Learning by taking Advice, Learning from examples, Explanation-Based
learning, Expert Systems & Its Architecture, Speech Recognition
10. Prolog: Introduction, Converting English to Prolog Facts and Rules, Goals, Prolog Terminology, Variables,
Control Structures, Arithmetic operators, Matching, Backtracking, Lists, Input/Output and Streams