Page 56 - DCAP508_DATABASE_ADMINISTRATION
P. 56
Database Administration
Notes SQL Server data and log files can be put on either FAT or NTFS file systems. We recommend
using the NTFS file system because the security aspects of NTFS. Read/write data filegroups and
log files cannot be placed on an NTFS compressed file system. Only read-only databases and
read-only secondary filegroups can be put on an NTFS compressed file system.
Task Differentiate between logical_file_name and os_file_name
When multiple instances of SQL Server are run on a single computer, each instance receives a
different default directory to hold the files for the databases created in the instance.
4.3.2 Data File Pages
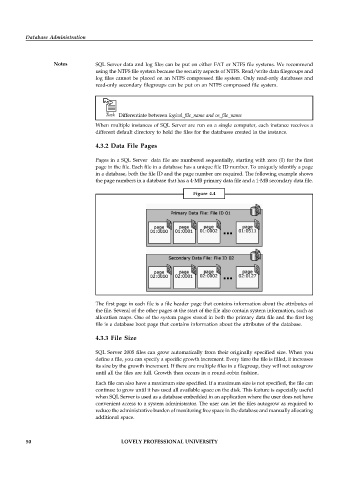
Pages in a SQL Server data file are numbered sequentially, starting with zero (0) for the first
page in the file. Each file in a database has a unique file ID number. To uniquely identify a page
in a database, both the file ID and the page number are required. The following example shows
the page numbers in a database that has a 4-MB primary data file and a 1-MB secondary data file.
Figure 4.4
The first page in each file is a file header page that contains information about the attributes of
the file. Several of the other pages at the start of the file also contain system information, such as
allocation maps. One of the system pages stored in both the primary data file and the first log
file is a database boot page that contains information about the attributes of the database.
4.3.3 File Size
SQL Server 2005 files can grow automatically from their originally specified size. When you
define a file, you can specify a specific growth increment. Every time the file is filled, it increases
its size by the growth increment. If there are multiple files in a filegroup, they will not autogrow
until all the files are full. Growth then occurs in a round-robin fashion.
Each file can also have a maximum size specified. If a maximum size is not specified, the file can
continue to grow until it has used all available space on the disk. This feature is especially useful
when SQL Server is used as a database embedded in an application where the user does not have
convenient access to a system administrator. The user can let the files autogrow as required to
reduce the administrative burden of monitoring free space in the database and manually allocating
additional space.
50 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY