Page 91 - DCAP508_DATABASE_ADMINISTRATION
P. 91
Unit 6: SQL Server Authentication
2. Mixed Mode (Windows Authentication and SQL Server Authentication): Mixed Mode Notes
allows users to connect to an instance of SQL Server using either Windows Authentication
or SQL Server Authentication. Users who connect through a Windows NT 4.0 or Windows
2000 user account can make use of trusted connections in either Windows Authentication
Mode or Mixed Mode.
SQL Server Authentication is provided for backward compatibility. For example, if you create a
single Windows 2000 group and add all necessary users to that group you will need to grant the
Windows 2000 group login rights to SQL Server and access to any necessary databases.
Security Note: When possible, use Windows Authentication.
6.1.1 Windows Authentication
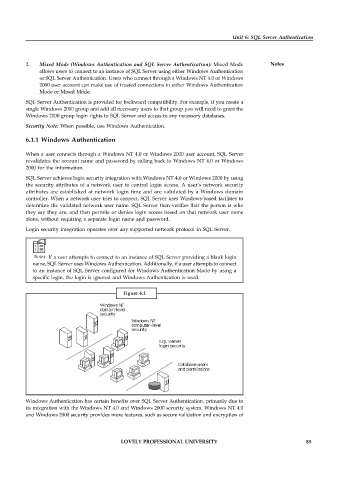
When a user connects through a Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 user account, SQL Server
revalidates the account name and password by calling back to Windows NT 4.0 or Windows
2000 for the information.
SQL Server achieves login security integration with Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 by using
the security attributes of a network user to control login access. A user’s network security
attributes are established at network login time and are validated by a Windows domain
controller. When a network user tries to connect, SQL Server uses Windows-based facilities to
determine the validated network user name. SQL Server then verifies that the person is who
they say they are, and then permits or denies login access based on that network user name
alone, without requiring a separate login name and password.
Login security integration operates over any supported network protocol in SQL Server.
Notes If a user attempts to connect to an instance of SQL Server providing a blank login
name, SQL Server uses Windows Authentication. Additionally, if a user attempts to connect
to an instance of SQL Server configured for Windows Authentication Mode by using a
specific login, the login is ignored and Windows Authentication is used.
Figure 6.1
Windows Authentication has certain benefits over SQL Server Authentication, primarily due to
its integration with the Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 security system. Windows NT 4.0
and Windows 2000 security provides more features, such as secure validation and encryption of
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 85