Page 102 - DCAP408_WEB_PROGRAMMING
P. 102
Windows Programming
Notes 7. The size of the database global memory is stated by the ...................... configuration
parameter.
8. You can fix ...................... to assign more memory than is required originally so that the
additional memory can be dynamically distributed afterwards.
9. The...................... parameter fixes an upper limit to the total number of database manager
agents in a database partition.
6.2 What Windows is actually Doing with Memory?
The first version of the Windows operating system established a technique of managing dynamic
memory relying on a single global heap, which all applications and the system share, and several,
private local heaps, one for every application. Local and global memory management functions
were also offered, providing extended traits for this new memory management system. More
lately, the Microsoft C run-time (CRT) libraries were customized to comprise capabilities for
administrating these heaps in Windows by means of native CRT functions like malloc and free.
Accordingly, developers are now left with an option—study the new application programming
interface (API) offered as part of Windows or stick to the transportable, and usually familiar,
CRT functions for managing memory in applications written for Windows.
Did u know? Window provides three groups of functions for managing memory in
applications: memory-mapped file functions, heap memory functions, and virtual-memory
functions.
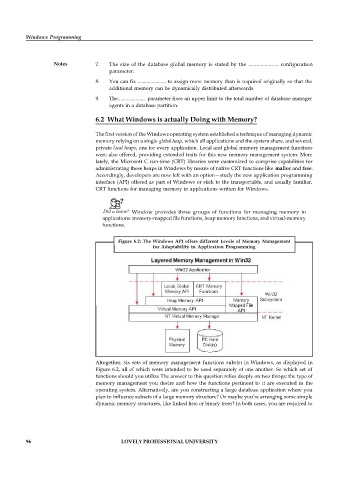
Figure 6.2: The Windows API offers different Levels of Memory Management
for Adaptability in Application Programming
Altogether, six sets of memory management functions subsist in Windows, as displayed in
Figure 6.2, all of which were intended to be used separately of one another. So which set of
functions should you utilize The answer to this question relies deeply on two things: the type of
memory management you desire and how the functions pertinent to it are executed in the
operating system. Alternatively, are you constructing a large database application where you
plan to influence subsets of a large memory structure? Or maybe you’re arranging some simple
dynamic memory structures, like linked lists or binary trees? In both cases, you are required to
96 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY