Page 4 - DCAP408_WEB_PROGRAMMING
P. 4
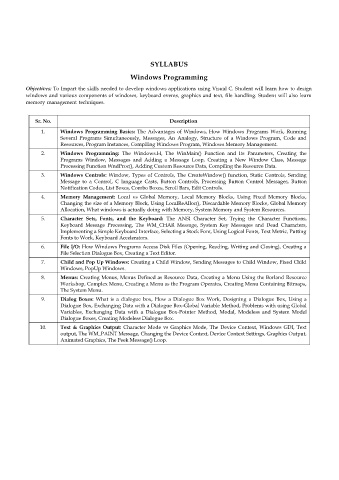
SYLLABUS
Windows Programming
Objectives: To Impart the skills needed to develop windows applications using Visual C. Student will learn how to design
windows and various components of windows, keyboard events, graphics and text, file handling. Student will also learn
memory management techniques.
Sr. No. Description
1. Windows Programming Basics: The Advantages of Windows, How Windows Programs Work, Running
Several Programs Simultaneously, Messages, An Analogy, Structure of a Windows Program, Code and
Resources, Program Instances, Compiling Windows Program, Windows Memory Management.
2. Windows Programming: The Windows.H, The WinMain() Function and Its Parameters, Creating the
Programs Window, Messages and Adding a Message Loop, Creating a New Window Class, Message
Processing Function WndProc(), Adding Custom Resource Data, Compiling the Resource Data.
3. Windows Controls: Window, Types of Controls, The CreateWindow() function, Static Controls, Sending
Message to a Control, C language Casts, Button Controls, Processing Button Control Messages, Button
Notification Codes, List Boxes, Combo Boxes, Scroll Bars, Edit Controls.
4. Memory Management: Local vs Global Memory, Local Memory Blocks, Using Fixed Memory Blocks,
Changing the size of a Memory Block, Using LocalReAlloc(), Discardable Memory Blocks, Global Memory
Allocation, What windows is actually doing with Memory, System Memory and System Resources.
5. Character Sets, Fonts, and the Keyboard: The ANSI Character Set, Trying the Character Functions,
Keyboard Message Processing, The WM_CHAR Message, System Key Messages and Dead Characters,
Implementing a Simple Keyboard Interface, Selecting a Stock Font, Using Logical Fonts, Text Metric, Putting
Fonts to Work, Keyboard Accelerators.
6. File I/O: How Windows Programs Access Disk Files (Opening, Reading, Writing and Closing), Creating a
File Selection Dialogue Box, Creating a Text Editor.
7. Child and Pop Up Windows: Creating a Child Window, Sending Messages to Child Window, Fixed Child
Windows, PopUp Windows.
8. Menus: Creating Menus, Menus Defined as Resource Data, Creating a Menu Using the Borland Resource
Workshop, Complex Menu, Creating a Menu as the Program Operates, Creating Menu Containing Bitmaps,
The System Menu.
9. Dialog Boxes: What is a dialogue box, How a Dialogue Box Work, Designing a Dialogue Box, Using a
Dialogue Box, Exchanging Data with a Dialogue Box-Global Variable Method, Problems with using Global
Variables, Exchanging Data with a Dialogue Box-Pointer Method, Modal, Modeless and System Modal
Dialogue Boxes, Creating Modeless Dialogue Box.
10. Text & Graphics Output: Character Mode vs Graphics Mode, The Device Context, Windows GDI, Text
output, The WM_PAINT Message, Changing the Device Context, Device Context Settings, Graphics Output,
Animated Graphics, The Peek Message() Loop.