Page 45 - DCAP408_WEB_PROGRAMMING
P. 45
Unit 3: Windows Programming
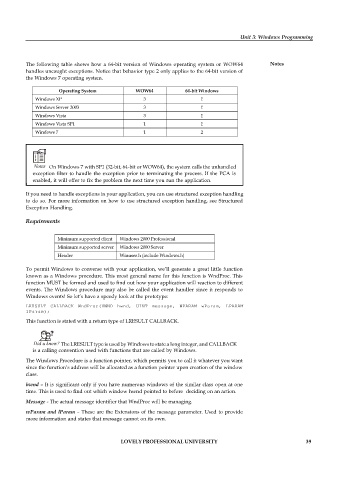
The following table shows how a 64-bit version of Windows operating system or WOW64 Notes
handles uncaught exceptions. Notice that behavior type 2 only applies to the 64-bit version of
the Windows 7 operating system.
Operating System WOW64 64-bit Windows
Windows XP 3 1
Windows Server 2003 3 1
Windows Vista 3 1
Windows Vista SP1 1 1
Windows 7 1 2
Notes On Windows 7 with SP1 (32-bit, 64-bit or WOW64), the system calls the unhandled
exception filter to handle the exception prior to terminating the process. If the PCA is
enabled, it will offer to fix the problem the next time you run the application.
If you need to handle exceptions in your application, you can use structured exception handling
to do so. For more information on how to use structured exception handling, see Structured
Exception Handling.
Requirements
Minimum supported client Windows 2000 Professional
Minimum supported server Windows 2000 Server
Header Winuser.h (include Windows.h)
To permit Windows to converse with your application, we’ll generate a great little function
known as a Windows procedure. This most general name for this function is WndProc. This
function MUST be formed and used to find out how your application will reaction to different
events. The Windows procedure may also be called the event handler since it responds to
Windows events! So let’s have a speedy look at the prototype:
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM
lParam);
This function is stated with a return type of LRESULT CALLBACK.
Did u know? The LRESULT type is used by Windows to state a long integer, and CALLBACK
is a calling convention used with functions that are called by Windows.
The Windows Procedure is a function pointer, which permits you to call it whatever you want
since the function’s address will be allocated as a function pointer upon creation of the window
class.
hwnd – It is significant only if you have numerous windows of the similar class open at one
time. This is used to find out which window hwnd pointed to before deciding on an action.
Message - The actual message identifier that WndProc will be managing.
wParam and lParam – These are the Extensions of the message parameter. Used to provide
more information and states that message cannot on its own.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 39