Page 66 - DCAP602_NETWORK_OPERATING_SYSTEMS_I
P. 66
Network Operating Systems-I
notes
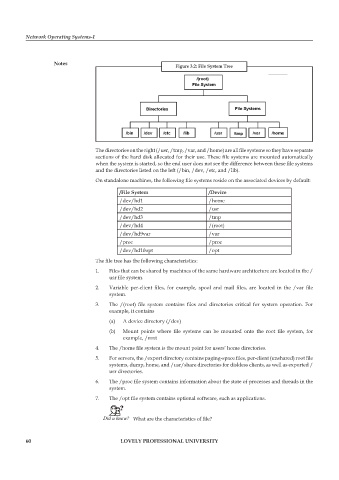
figure 3.2: file system tree
The directories on the right (/usr, /tmp, /var, and /home) are all file systems so they have separate
sections of the hard disk allocated for their use. These file systems are mounted automatically
when the system is started, so the end user does not see the difference between these file systems
and the directories listed on the left (/bin, /dev, /etc, and /lib).
On standalone machines, the following file systems reside on the associated devices by default:
/file system /Device
/dev/hd1 /home
/dev/hd2 /usr
/dev/hd3 /tmp
/dev/hd4 /(root)
/dev/hd9var /var
/proc /proc
/dev/hd10opt /opt
The file tree has the following characteristics:
1. Files that can be shared by machines of the same hardware architecture are located in the /
usr file system.
2. Variable per-client files, for example, spool and mail files, are located in the /var file
system.
3. The /(root) file system contains files and directories critical for system operation. For
example, it contains
(a) A device directory (/dev)
(b) Mount points where file systems can be mounted onto the root file system, for
example, /mnt
4. The /home file system is the mount point for users’ home directories.
5. For servers, the /export directory contains paging-space files, per-client (unshared) root file
systems, dump, home, and /usr/share directories for diskless clients, as well as exported /
usr directories.
6. The /proc file system contains information about the state of processes and threads in the
system.
7. The /opt file system contains optional software, such as applications.
Did u know? What are the characteristics of file?
60 LoveLy professionaL university