Page 172 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 172
Data Warehousing and Data Mining
notes the need for Materialized views
You can use materialized views to increase the speed of queries on very large databases. Queries
to large databases often involve joins between tables, aggregations such as SUM, or both. These
operations are expensive in terms of time and processing power. The type of materialized view
you create determines how the materialized view is refreshed and used by query rewrite.
Materialized views improve query performance by pre-calculating expensive join and aggregation
operations on the database prior to execution and storing the results in the database. The
query optimizer automatically recognizes when an existing materialized view can and should
be used to satisfy a request. It then transparently rewrites the request to use the materialized
view. Queries go directly to the materialized view and not to the underlying detail tables. In
general, rewriting queries to use materialized views rather than detail tables improves response.
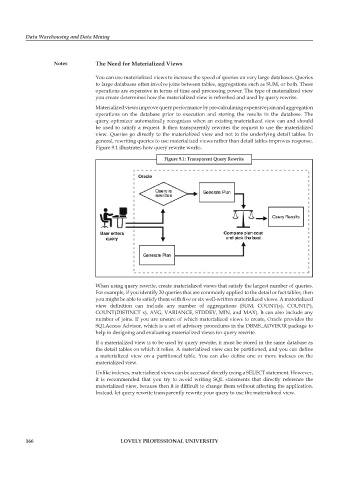
Figure 9.1 illustrates how query rewrite works.
figure 9.1: transparent Query rewrite
When using query rewrite, create materialized views that satisfy the largest number of queries.
For example, if you identify 20 queries that are commonly applied to the detail or fact tables, then
you might be able to satisfy them with five or six well-written materialized views. A materialized
view definition can include any number of aggregations (SUM, COUNT(x), COUNT(*),
COUNT(DISTINCT x), AVG, VARIANCE, STDDEV, MIN, and MAX). It can also include any
number of joins. If you are unsure of which materialized views to create, Oracle provides the
SQLAccess Advisor, which is a set of advisory procedures in the DBMS_ADVISOR package to
help in designing and evaluating materialized views for query rewrite.
If a materialized view is to be used by query rewrite, it must be stored in the same database as
the detail tables on which it relies. A materialized view can be partitioned, and you can define
a materialized view on a partitioned table. You can also define one or more indexes on the
materialized view.
Unlike indexes, materialized views can be accessed directly using a SELECT statement. However,
it is recommended that you try to avoid writing SQL statements that directly reference the
materialized view, because then it is difficult to change them without affecting the application.
Instead, let query rewrite transparently rewrite your query to use the materialized view.
166 LoveLy professionaL university