Page 180 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 180
Data Warehousing and Data Mining
notes Data Loading vs. Data Refreshment
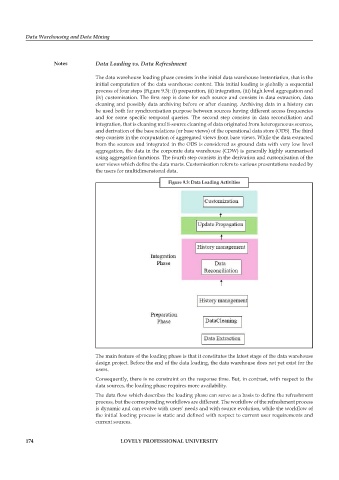
The data warehouse loading phase consists in the initial data warehouse instantiation, that is the
initial computation of the data warehouse content. This initial loading is globally a sequential
process of four steps (Figure 9.3): (i) preparation, (ii) integration, (iii) high level aggregation and
(iv) customisation. The first step is done for each source and consists in data extraction, data
cleaning and possibly data archiving before or after cleaning. Archiving data in a history can
be used both for synchronisation purpose between sources having different access frequencies
and for some specific temporal queries. The second step consists in data reconciliation and
integration, that is cleaning multi-source cleaning of data originated from heterogeneous sources,
and derivation of the base relations (or base views) of the operational data store (ODS). The third
step consists in the computation of aggregated views from base views. While the data extracted
from the sources and integrated in the ODS is considered as ground data with very low level
aggregation, the data in the corporate data warehouse (CDW) is generally highly summarised
using aggregation functions. The fourth step consists in the derivation and customisation of the
user views which define the data marts. Customisation refers to various presentations needed by
the users for multidimensional data.
figure 9.3: Data Loading activities
The main feature of the loading phase is that it constitutes the latest stage of the data warehouse
design project. Before the end of the data loading, the data warehouse does not yet exist for the
users.
Consequently, there is no constraint on the response time. But, in contrast, with respect to the
data sources, the loading phase requires more availability.
The data flow which describes the loading phase can serve as a basis to define the refreshment
process, but the corresponding workflows are different. The workflow of the refreshment process
is dynamic and can evolve with users’ needs and with source evolution, while the workflow of
the initial loading process is static and defined with respect to current user requirements and
current sources.
174 LoveLy professionaL university