Page 219 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 219
Unit 11: Query Processing and Optimization
notes
Example:
CostModel (Inverted Partitioned Index) = Access Time of Index Level + Instruction
Time (Inverted Partitioned Index)
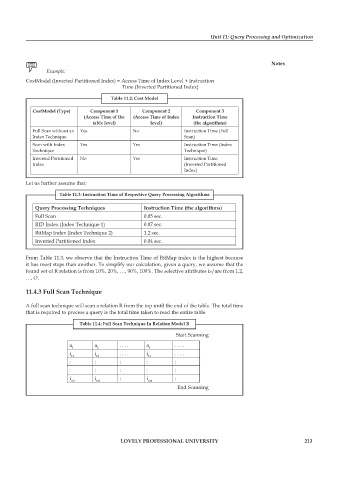
table 11.2: cost Model
costModel (type) component 1 component 2 component 3
(access time of the (access time of index instruction time
table level) level) (the algorithms)
Full Scan without an Yes No Instruction Time (Full
Index Technique Scan)
Scan with Index Yes Yes Instruction Time (Index
Technique Technique)
Inverted Partitioned No Yes Instruction Time
Index (Inverted Partitioned
Index)
Let us further assume that:
table 11.3: instruction time of respective Query processing algorithms
Query processing techniques instruction time (the algorithms)
Full Scan 0.05 sec.
RID Index (Index Technique 1) 0.07 sec.
BitMap Index (Index Technique 2) 1.2 sec.
Inverted Partitioned Index 0.04 sec.
From Table 11.3, we observe that the Instruction Time of BitMap index is the highest because
it has most steps than another. To simplify our calculation, given a query, we assume that the
found set of R relation is from 10%, 20%, …, 90%, 100%. The selective attributes is/are from 1,2,
…, O.
11.4.3 full scan technique
A full scan technique will scan a relation R from the top until the end of the table. The total time
that is required to process a query is the total time taken to read the entire table.
table 11.4: full scan technique in relation Model r
Start Scanning
a a . . . . a . . . .
1 2 4
i i . . . . i . . . .
11 12 14
: : : : :
: : : : :
i m1 i m2 : i m4 :
End Scanning
LoveLy professionaL university 213