Page 251 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 251
Unit 13: Metadata and Data Warehouse Quality
13.1 representing and analyzing Data Warehouse Quality notes
Data quality (DQ) is an extremely important issue since quality determines the data’s usefulness
as well as the quality of the decisions based on the data. It has the following dimensions: accuracy,
accessibility, relevance, timeliness, and completeness. Data are frequently found to be inaccurate,
incomplete, or ambiguous, particularly in large, centralized databases. The economical and social
damage from poor-quality data has actually been calculated to have cost organizations billions of
dollars, data quality is the cornerstone of effective business intelligence.
Interest in data quality has been known for generations. For example, according to Hasan (2002),
treatment of numerical data for quality can be traced to the year 1881. An example of typical data
problems, their causes, and possible solutions is provided in Table 13.1.
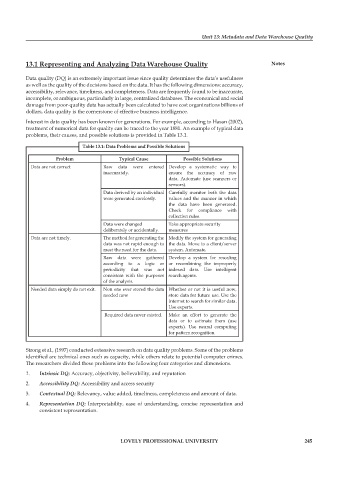
table 13.1: Data problems and possible solutions
problem typical cause possible solutions
Data are not correct Raw data were entered Develop a systematic way to
inaccurately. ensure the accuracy of raw
data. Automate (use scanners or
sensors).
Data derived by an individual Carefully monitor both the data
were generated carelessly. values and the manner in which
the data have been generated.
Check for compliance with
collection rules.
Data were changed Take appropriate security
deliberately or accidentally. measures
Data are not timely. The method for generating the Modify the system for generating
data was not rapid enough to the data. Move to a client/server
meet the need for the data. system. Automate.
Raw data were gathered Develop a system for rescaling
according to a logic or or recombining the improperly
periodicity that was not indexed data. Use intelligent
consistent with the purposes search agents.
of the analysis.
Needed data simply do not exit. Non one ever stored the data Whether or not it is useful now,
needed now store data for future use. Use the
Internet to search for similar data.
Use experts.
Required data never existed. Make an effort to generate the
data or to estimate them (use
experts). Use neural computing
for pattern recognition.
Strong et al., (1997) conducted extensive research on data quality problems. Some of the problems
identified are technical ones such as capacity, while others relate to potential computer crimes.
The researchers divided these problems into the following four categories and dimensions.
1. Intrinsic DQ: Accuracy, objectivity, believability, and reputation
2. Accessibility DQ: Accessibility and access security
3. Contextual DQ: Relevancy, value added, timeliness, completeness and amount of data.
4. Representation DQ: Interpretability, ease of understanding, concise representation and
consistent representation.
LoveLy professionaL university 245