Page 84 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 84
Data Warehousing and Data Mining
notes common in mammals. Examples of these neurons are spinal motor neurons, pyramidal cells and
Purkinje cells (in the cerebellum). If classified by function, neurons again fall into three separate
categories. The first group is sensory, or afferent, neurons, which provide information for
perception and motor coordination. The second group provides information (or instructions) to
muscles and glands and is therefore called motor neurons. The last group, interneuronal, contains
all other neurons and has two subclasses. One group called relay or projection interneurons have
long axons and connect different parts of the brain. The other group called local interneurons are
only used in local circuits.
the Mathematical Model
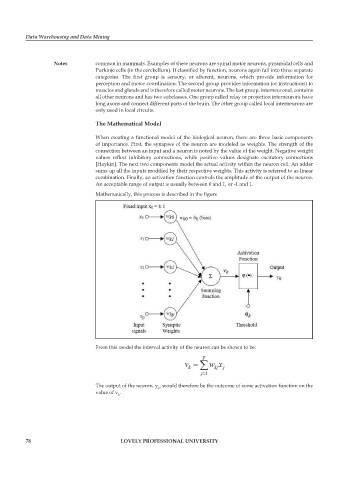
When creating a functional model of the biological neuron, there are three basic components
of importance. First, the synapses of the neuron are modeled as weights. The strength of the
connection between an input and a neuron is noted by the value of the weight. Negative weight
values reflect inhibitory connections, while positive values designate excitatory connections
[Haykin]. The next two components model the actual activity within the neuron cell. An adder
sums up all the inputs modified by their respective weights. This activity is referred to as linear
combination. Finally, an activation function controls the amplitude of the output of the neuron.
An acceptable range of output is usually between 0 and 1, or -1 and 1.
Mathematically, this process is described in the figure
From this model the interval activity of the neuron can be shown to be:
The output of the neuron, y , would therefore be the outcome of some activation function on the
k
value of v .
k
78 LoveLy professionaL university