Page 99 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 99
Unit 5: Data Warehouse Research – Issues and Research
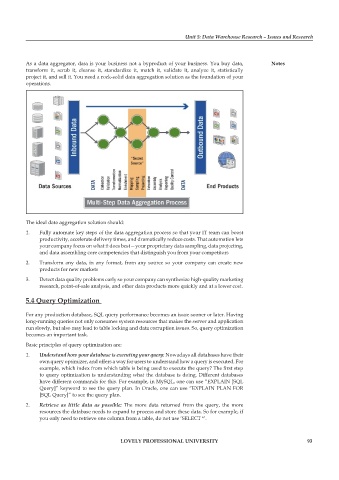
As a data aggregator, data is your business not a byproduct of your business. You buy data, notes
transform it, scrub it, cleanse it, standardize it, match it, validate it, analyze it, statistically
project it, and sell it. You need a rock-solid data aggregation solution as the foundation of your
operations.
The ideal data aggregation solution should:
1. Fully automate key steps of the data aggregation process so that your IT team can boost
productivity, accelerate delivery times, and dramatically reduce costs. That automation lets
your company focus on what it does best—your proprietary data sampling, data projecting,
and data assembling core competencies that distinguish you from your competitors
2. Transform any data, in any format, from any source so your company can create new
products for new markets
3. Detect data quality problems early so your company can synthesize high-quality marketing
research, point-of-sale analysis, and other data products more quickly and at a lower cost.
5.4 Query optimization
For any production database, SQL query performance becomes an issue sooner or later. Having
long-running queries not only consumes system resources that makes the server and application
run slowly, but also may lead to table locking and data corruption issues. So, query optimization
becomes an important task.
Basic principles of query optimization are:
1. Understand how your database is executing your query: Nowadays all databases have their
own query optimizer, and offers a way for users to understand how a query is executed. For
example, which index from which table is being used to execute the query? The first step
to query optimization is understanding what the database is doing. Different databases
have different commands for this. For example, in MySQL, one can use “EXPLAIN [SQL
Query]” keyword to see the query plan. In Oracle, one can use “EXPLAIN PLAN FOR
[SQL Query]” to see the query plan.
2. Retrieve as little data as possible: The more data returned from the query, the more
resources the database needs to expand to process and store these data. So for example, if
you only need to retrieve one column from a table, do not use ‘SELECT *’.
LoveLy professionaL university 93