Page 232 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 232
Unit 11: Leftist Heaps and Binomial Queues
worst-case time bound for each of the heap operations, where n is the number of nodes in the Notes
heap or heaps involved.
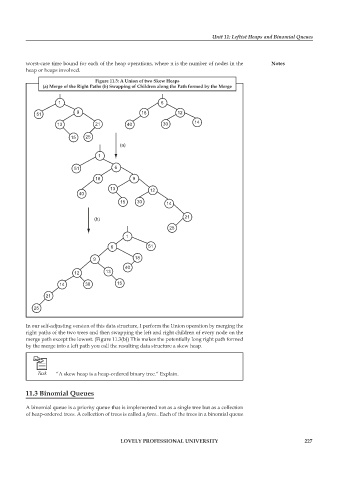
Figure 11.3: A Union of two Skew Heaps
(a) Merge of the Right Paths (b) Swapping of Children along the Path formed by the Merge
1 6
9 18 12
51
13 21 40 30 14
15 25
(a)
1
51 6
18 9
13 12
40
15 30 14
21
(b)
25
1
6 51
9 18
40
12 13
14 30 15
21
25
In our self-adjusting version of this data structure, I perform the Union operation by merging the
right paths of the two trees and then swapping the left and right children of every node on the
merge path except the lowest. (Figure 11.3(b)) This makes the potentially long right path formed
by the merge into a left path you call the resulting data structure a skew heap.
Task “A skew heap is a heap-ordered binary tree.” Explain.
11.3 Binomial Queues
A binomial queue is a priority queue that is implemented not as a single tree but as a collection
of heap-ordered trees. A collection of trees is called a fores.. Each of the trees in a binomial queue
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 227