Page 51 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 51
Advanced Data Structure and Algorithms
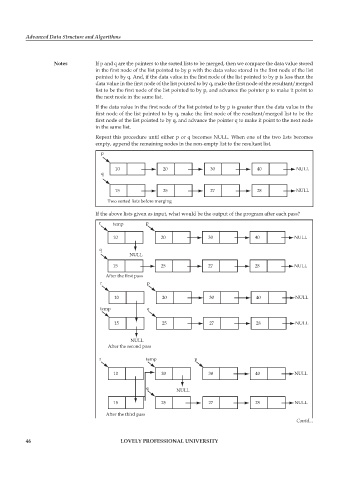
Notes If p and q are the pointers to the sorted lists to be merged, then we compare the data value stored
in the first node of the list pointed to by p with the data value stored in the first node of the list
pointed to by q. And, if the data value in the first node of the list pointed to by p is less than the
data value in the first node of the list pointed to by q, make the first node of the resultant/merged
list to be the first node of the list pointed to by p, and advance the pointer p to make it point to
the next node in the same list.
If the data value in the first node of the list pointed to by p is greater than the data value in the
first node of the list pointed to by q, make the first node of the resultant/merged list to be the
first node of the list pointed to by q, and advance the pointer q to make it point to the next node
in the same list.
Repeat this procedure until either p or q becomes NULL. When one of the two lists becomes
empty, append the remaining nodes in the non-empty list to the resultant list.
p
10 20 30 40 NULL
q
15 25 27 28 NULL
Two sorted lists before merging
If the above lists given as input, what would be the output of the program after each pass?
r temp p
10 20 30 40 NULL
q
NULL
15 25 27 28 NULL
After the first pass
r p
10 20 30 40 NULL
temp q
15 25 27 28 NULL
NULL
After the second pass
r temp p
10 20 30 40 NULL
q
NULL
15 25 27 28 NULL
After the third pass
Contd...
46 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY