Page 57 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 57
Advanced Data Structure and Algorithms
Notes int exp;
struct poly link;
}
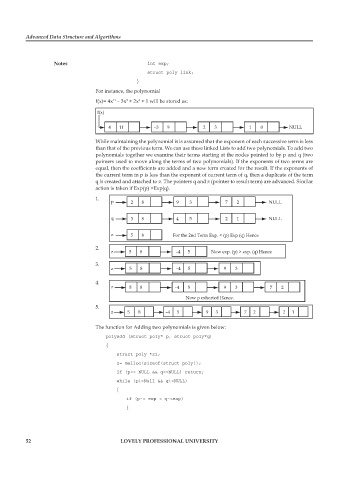
For instance, the polynomial
3
11
f(x)= 4x – 3x + 2x + 1 will be stored as:
9
f(x)
4 11 –3 9 2 3 1 0 NULL
While maintaining the polynomial it is assumed that the exponent of each successive term is less
than that of the previous term. We can use these linked Lists to add two polynomials. To add two
polynomials together we examine their terms starting at the nodes pointed to by p and q (two
pointers used to move along the terms of two polynomials). If the exponents of two terms are
equal, then the coefficients are added and a new term created for the result. If the exponents of
the current term in p is less than the exponent of current term of q, then a duplicate of the term
q is created and attached to z. The pointers q and z (pointer to result term) are advanced. Similar
action is taken if Exp(p) >Exp(q).
1.
p 2 8 9 3 7 2 NULL
q 3 8 4 5 2 1 NULL
z 5 8 For the 2nd Term Exp. < (p) Exp (q) Hence
2.
z 5 8 –4 5 Now exp. (p) > exp. (q) Hence
3.
z 5 8 –4 5 9 3
4.
z 5 8 –4 5 9 3 7 2
Now p exhorted Hence.
5.
z 5 8 –4 5 9 3 7 2 2 1
The function for Adding two polynomials is given below:
polyadd (struct poly* p, struct poly*q)
{
struct poly *z1;
z= malloc(sizeof(struct poly));
if (p== NULL && q==NULL) return;
while (p!=Null && q!=NULL)
{
if (p-> exp > q->exp)
{
52 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY