Page 137 - DCAP311_DCAP607_WIRELESS_NETWORKS
P. 137
Unit 8: Wireless MAN
For example, to provide wireless connectivity for a group of network printers, connect the Notes
printers to a hub or to a switch, connect the hub or switch to the Ethernet port of the workgroup
bridge. The workgroup bridge transfers data through its association with an access point or
bridge on the network.
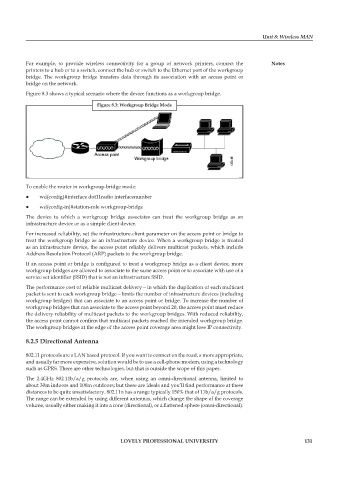
Figure 8.3 shows a typical scenario where the device functions as a workgroup bridge.
Figure 8.3: Workgroup Bridge Mode
To enable the router in workgroup-bridge mode:
z z wd(config)#interface dot11radio interfacenumber
z z wd(config-in)#station-role workgroup-bridge
The device to which a workgroup bridge associates can treat the workgroup bridge as an
infrastructure device or as a simple client device.
For increased reliability, set the infrastructure-client parameter on the access point or bridge to
treat the workgroup bridge as an infrastructure device. When a workgroup bridge is treated
as an infrastructure device, the access point reliably delivers multicast packets, which include
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packets to the workgroup bridge.
If an access point or bridge is configured to treat a workgroup bridge as a client device, more
workgroup bridges are allowed to associate to the same access point or to associate with use of a
service set identifier (SSID) that is not an infrastructure SSID.
The performance cost of reliable multicast delivery—in which the duplication of each multicast
packet is sent to each workgroup bridge—limits the number of infrastructure devices (including
workgroup bridges) that can associate to an access point or bridge. To increase the number of
workgroup bridges that can associate to the access point beyond 20, the access point must reduce
the delivery reliability of multicast packets to the workgroup bridges. With reduced reliability,
the access point cannot confirm that multicast packets reached the intended workgroup bridge.
The workgroup bridges at the edge of the access point coverage area might lose IP connectivity.
8.2.5 Directional Antenna
802.11 protocols are a LAN based protocol. If you want to connect on the road, a more appropriate,
and usually far more expensive, solution would be to use a cell-phone modem, using a technology
such as GPRS. There are other technologies, but that is outside the scope of this paper.
The 2.4GHz 802.11b/a/g protocols are, when using an omni-directional antenna, limited to
about 30m indoors and 100m outdoors; but these are ideals and you’ll find performance at these
distances to be quite unsatisfactory. 802.11n has a range typically 150% that of 11b/a/g protocols.
The range can be extended by using different antennas, which change the shape of the coverage
volume, usually either making it into a cone (directional), or a flattened sphere (omni-directional).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 131