Page 13 - DCAP609_CLOUD_COMPUTING
P. 13
Cloud Computing
Notes 1.3 Working of Cloud Computing
Sun NVlicrosystems’s slogan is “The network is the computer,” and that is as good as any to
describe how cloud computing works. In essence, a network of computers functions as a single
computer to serve data and applications to users over the Internet. The network exists in the
“cloud” of IP addresses that we know as the Internet, offers massive computing power and
storage capability, and enables wide scale group collaboration.
But that is the simple explanation. Let us take a look at how cloud computing works in more
detail.
1.3.1 Cloud Architecture
Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and subcomponents required for cloud
computing. These components typically consist of a front end platform (fat client, thin client,
mobile device), back end platforms (servers, storage), a cloud based delivery, and a network
(Internet, Intranet, Intercloud). Combined, these components make up cloud computing
architecture.
The zero or ultra-thin client initializes the network to gather required configuration files that
then tell it where its OS binaries are stored. The entire zero client device runs via the network.
This creates a single point of failure, in that, if the network goes down, the device is rendered
useless.
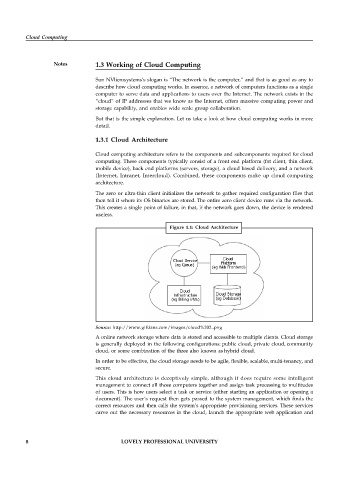
Figure 1.1: Cloud Architecture
Source: http://www.giftians.com/images/cloud%202..png
A online network storage where data is stored and accessible to multiple clients. Cloud storage
is generally deployed in the following configurations: public cloud, private cloud, community
cloud, or some combination of the three also known as hybrid cloud.
In order to be effective, the cloud storage needs to be agile, flexible, scalable, multi-tenancy, and
secure.
This cloud architecture is deceptively simple, although it does require some intelligent
management to connect all those computers together and assign task processing to multitudes
of users. This is how users select a task or service (either starting an application or opening a
document). The user’s request then gets passed to the system management, which finds the
correct resources and then calls the system’s appropriate provisioning services. These services
carve out the necessary resources in the cloud, launch the appropriate web application and
8 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY