Page 6 - DCAP102_DCAP_401_Foundations of Computer Programming
P. 6
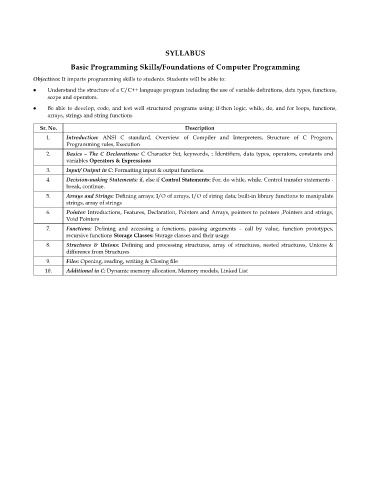
SYLLABUS
Basic Programming Skills/Foundations of Computer Programming
Objectives: It imparts programming skills to students. Students will be able to:
Understand the structure of a C/C++ language program including the use of variable definitions, data types, functions,
scope and operators.
Be able to develop, code, and test well structured programs using: if-then logic, while, do, and for loops, functions,
arrays, strings and string functions
Sr. No. Description
1. Introduction: ANSI C standard, Overview of Compiler and Interpreters, Structure of C Program,
Programming rules, Execution
2. Basics – The C Declarations: C Character Set, keywords, : Identifiers, data types, operators, constants and
variables Operators & Expressions
3. Input/ Output in C: Formatting input & output functions.
4. Decision-making Statements: if, else if Control Statements: For, do while, while. Control transfer statements -
break, continue.
5. Arrays and Strings: Defining arrays; I/O of arrays, I/O of string data; built-in library functions to manipulate
strings, array of strings
6. Pointer: Introductions, Features, Declaration, Pointers and Arrays, pointers to pointers ,Pointers and strings,
Void Pointers
7. Functions: Defining and accessing a functions, passing arguments – call by value, function prototypes,
recursive functions Storage Classes: Storage classes and their usage
8. Structures & Unions: Defining and processing structures, array of structures, nested structures, Unions &
difference from Structures
9. Files: Opening, reading, writing & Closing file
10. Additional in C: Dynamic memory allocation, Memory models, Linked List