Page 292 - DCAP403_Operating System
P. 292
Unit 13: Case Study: Linux
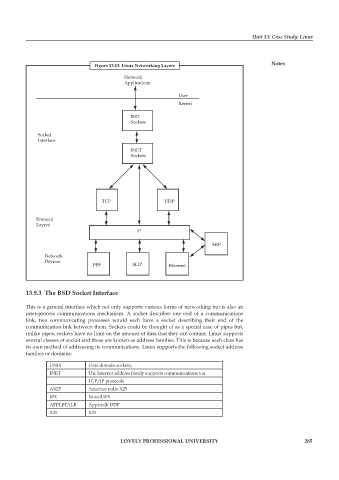
Figure 13.13: Linux Networking Layers Notes
Network
Applications
User
Kernel
BSD
Sockets
Socket
Interface
INET
Sockets
TCP UDP
Protocol
Layers
IP
ARP
Network
Devices
PPP SLIP Ethernet
13.9.3 The BSD Socket Interface
This is a general interface which not only supports various forms of networking but is also an
inter-process communications mechanism. A socket describes one end of a communications
link, two communicating processes would each have a socket describing their end of the
communication link between them. Sockets could be thought of as a special case of pipes but,
unlike pipes, sockets have no limit on the amount of data that they can contain. Linux supports
several classes of socket and these are known as address families. This is because each class has
its own method of addressing its communications. Linux supports the following socket address
families or domains:
UNIX Unix domain sockets,
INET The Internet address family supports communications via
TCP/IP protocols
AX25 Amateur radio X25
IPX Novell IPX
APPLETALK Appletalk DDP
X25 X25
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 285