Page 229 - DENG401_Advance Communication Skills
P. 229
Advanced Communication Skills
Notes
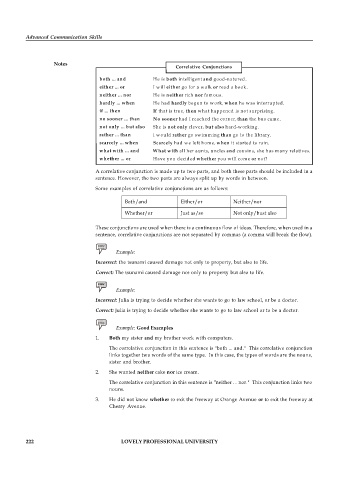
Correlative Conjunctions
both ... and He is both intelligent and good-natured.
either ... or I will either go for a walk or read a book.
neither ... nor He is neither rich nor famous.
hardly ... when He had hardly begun to work, when he was interrupted.
if ... then If that is true, then what happened is not surprising.
no sooner ... than No sooner had I reached the corner, than the bus came.
not only ... but also She is not only clever, but also hard-working.
rather ... than I would rather go swimming than go to the library.
scarcely ... when Scarcely had we left home, when it started to rain.
what with ... and What with all her aunts, uncles and cousins, she has many relatives.
whether ... or Have you decided whether you will come or not?
A correlative conjunction is made up to two parts, and both these parts should be included in a
sentence. However, the two parts are always split up by words in between.
Some examples of correlative conjunctions are as follows:
Both/and Either/or Neither/nor
Whether/or Just as/so Not only/bust also
These conjunctions are used when there is a continuous flow of ideas. Therefore, when used in a
sentence, correlative conjunctions are not separated by commas (a comma will break the flow).
Example:
Incorrect: the tsunami caused damage not only to property, but also to life.
Correct: The tsunami caused damage not only to property but also to life.
Example:
Incorrect: Julia is trying to decide whether she wants to go to law school, or be a doctor.
Correct: Julia is trying to decide whether she wants to go to law school or to be a doctor.
Example: Good Examples
1. Both my sister and my brother work with computers.
The correlative conjunction in this sentence is "both ... and." This correlative conjunction
links together two words of the same type. In this case, the types of words are the nouns,
sister and brother.
2. She wanted neither cake nor ice cream.
The correlative conjunction in this sentence is "neither ... nor." This conjunction links two
nouns.
3. He did not know whether to exit the freeway at Orange Avenue or to exit the freeway at
Cherry Avenue.
222 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY