Page 124 - DMGT409Basic Financial Management
P. 124
Unit 7: Capital Budgeting
Solution: Notes
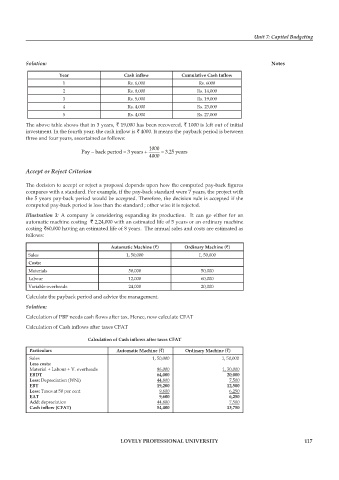
Year Cash inflow Cumulative Cash Infl ow
1 Rs. 6,000 Rs. 6000
2 Rs. 8,000 Rs. 14,000
3 Rs. 5,000 Rs. 19,000
4 Rs. 4,000 Rs. 23,000
5 Rs. 4,000 Rs. 27,000
The above table shows that in 3 years, ` 19,000 has been recovered, ` 1000 is left out of initial
investment. In the fourth year, the cash infl ow is ` 4000. It means the payback period is between
three and four years, ascertained as follows:
1000
Pay − back period = 3 years + = 3.25 years
4000
Accept or Reject Criterion
The decision to accept or reject a proposal depends upon how the computed pay-back fi gures
compares with a standard. For example, if the pay-back standard were 7 years, the project with
the 5 years pay-back period would be accepted. Therefore, the decision rule is accepted if the
computed pay-back period is less than the standard ; other wise it is rejected.
Illustration 3: A company is considering expanding its production. It can go either for an
automatic machine costing ` 2,24,000 with an estimated life of 5 years or an ordinary machine
costing `60,000 having an estimated life of 8 years. The annual sales and costs are estimated as
follows:
Automatic Machine (`) Ordinary Machine (`)
Sales 1, 50,000 1, 50,000
Costs:
Materials 50,000 50,000
Labour 12,000 60,000
Variable overheads 24,000 20,000
Calculate the payback period and advice the management.
Solution:
Calculation of PBP needs cash flows after tax. Hence, now calculate CFAT
Calculation of Cash inflows after taxes CFAT
Calculation of Cash inflows after taxes CFAT
Particulars Automatic Machine (`) Ordinary Machine (`)
Sales 1, 50,000 1, 50,000
Less costs:
Material + Labour + V. overheads 86,000 1, 30,000
EBDT 64,000 20,000
Less: Depreciation (WNi) 44,800 7,500
EBT 19,200 12,500
Less: Taxes at 50 per cent 9,600 6,250
EAT 9,600 6,250
Add: depreciation 44,800 7,500
Cash infl ow (CFAT) 54,400 13,750
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 117