Page 121 - DCAP406_DCAP_207_Computer Networks
P. 121
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes sending equipment how much data has been received, therefore, it is necessary to attach a
sequence number to each piece of data.
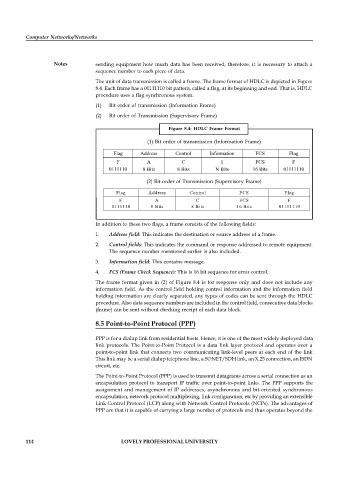
The unit of data transmission is called a frame. The frame format of HDLC is depicted in Figure
8.4. Each frame has a 01111110 bit pattern, called a flag, at its beginning and end. That is, HDLC
procedure uses a flag synchronous system.
(1) Bit order of transmission (Information Frame)
(2) Bit order of Transmission (Supervisory Frame)
Figure 8.4: HDLC Frame Format
(1) Bit order of transmission (Information Frame)
Flag Address Control Information FCS Flag
F A C I FCS F
0111110 8 Bits 8 Bits N Bits 16 Bits 01111110
(2) Bit order of Transmission (Supervisory Frame)
Flag Address Control FCS Flag
F A C FCS F
0111110 8 Bits 8 Bits 16 Bits 01111110
In addition to these two flags, a frame consists of the following fields:
1. Address field: This indicates the destination or source address of a frame.
2. Control fields: This indicates the command or response addressed to remote equipment.
The sequence number mentioned earlier is also included.
3. Information field: This contains message.
4. FCS (Frame Check Sequence): This is 16 bit sequence for error control.
The frame format given in (2) of Figure 8.4 is for response only and does not include any
information field. As the control field holding control information and the information field
holding information are clearly separated, any types of codes can be sent through the HDLC
procedure. Also data sequence numbers are included in the control field, consecutive data blocks
(frame) can be sent without checking receipt of each data block.
8.5 Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
PPP is for a dialup link from residential hosts. Hence, it is one of the most widely deployed data
link protocols. The Point-to-Point Protocol is a data link layer protocol and operates over a
point-to-point link that connects two communicating link-level peers at each end of the link
This link may be a serial dialup telephone line, a SONET/SDH link, an X.25 connection, an ISDN
circuit, etc.
The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is used to transmit datagrams across a serial connection as an
encapsulation protocol to transport IP traffic over point-to-point links. The PPP supports the
assignment and management of IP addresses, asynchronous and bit-oriented synchronous
encapsulation, network protocol multiplexing, link configuration, etc by providing an extensible
Link Control Protocol (LCP) along with Network Control Protocols (NCPs). The advantages of
PPP are that it is capable of carrying a large number of protocols and thus operates beyond the
114 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY