Page 78 - DCAP406_DCAP_207_Computer Networks
P. 78
Unit 5: Networking Devices
transfer, a dedicated connection is established for the transfer of data. At the end of the data Notes
transfer, the connection is broken. In this manner, the circuit switching provides a fixed data rate
channel for the source and destination devices. The circuit switching technique has disadvantages
over packet switching technique because of wastage of bandwidth when there is no data for
transmission at any moment of time. Moreover, setting up of connection also takes time. Circuit
switching involves datagram and data-stream transmissions. Datagram transmissions have
frames that are individually addressed. Data-stream transmissions do not have frames. They
have a data stream for which address checking occurs only once. The routing may be either static
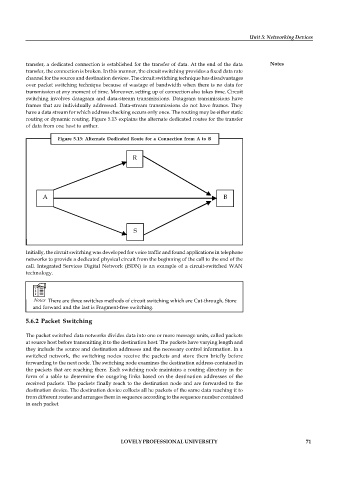
routing or dynamic routing. Figure 5.13 explains the alternate dedicated routes for the transfer
of data from one host to anther.
Figure 5.13: Alternate Dedicated Route for a Connection from A to B
R
A B
S
Initially, the circuit switching was developed for voice traffic and found applications in telephone
Figure 10.4 Alternate dedicated route for a connection from A to B
networks to provide a dedicated physical circuit from the beginning of the call to the end of the
call. Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is an example of a circuit-switched WAN
technology.
Notes There are three switches methods of circuit switching which are Cut-through, Store
and forward and the last is Fragment-free switching.
5.6.2 Packet Switching
The packet switched data networks divides data into one or more message units, called packets
at source host before transmitting it to the destination host. The packets have varying length and
they include the source and destination addresses and the necessary control information. In a
switched network, the switching nodes receive the packets and store them briefly before
forwarding to the next node. The switching node examines the destination address contained in
the packets that are reaching there. Each switching node maintains a routing directory in the
form of a table to determine the outgoing links based on the destination addresses of the
received packets. The packets finally reach to the destination node and are forwarded to the
destination device. The destination device collects all he packets of the same data reaching it to
from different routes and arranges them in sequence according to the sequence number contained
in each packet.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 71