Page 81 - DCAP306_DCAP511_E-COMMERCE_AND_E-BUSINESS
P. 81
E-Commerce and E-Business
pq-1 is divisible by (a-1) and (b-1).
The public and private keys are thus formed, (L, p) is the public key and (L, q) is the private key.
In order to encrypt an information I using the public key (L, p), calculate the value
This gives the encrypted information say E.
To decrypt information, calculate . This gives the original information I.
6.2.3 Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are used for verifying both authenticity and integrity of the information. When an
information transfer occurs over a communication network, care should be taken to prevent the (misuse
of the signature) receiver from using the sender’s signature to send the information to other sources on
behalf of the sender.
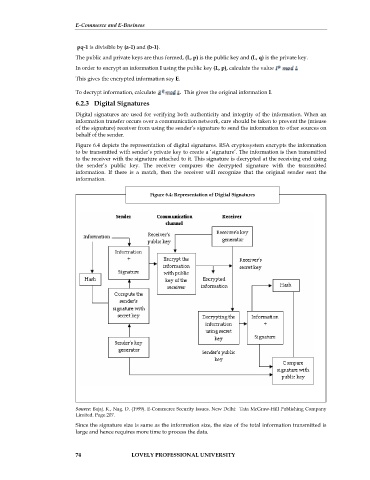
Figure 6.4 depicts the representation of digital signatures. RSA cryptosystem encrypts the information
to be transmitted with sender’s private key to create a ‘signature’. The information is then transmitted
to the receiver with the signature attached to it. This signature is decrypted at the receiving end using
the sender’s public key. The receiver compares the decrypted signature with the transmitted
information. If there is a match, then the receiver will recognize that the original sender sent the
information.
Figure 6.4: Representation of Digital Signatures
Source: Bajaj. K., Nag. D. (1999). E-Commerce Security Issues. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company
Limited. Page 207.
Since the signature size is same as the information size, the size of the total information transmitted is
large and hence requires more time to process the data.
74 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY