Page 196 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 196
Unit 10: Trees
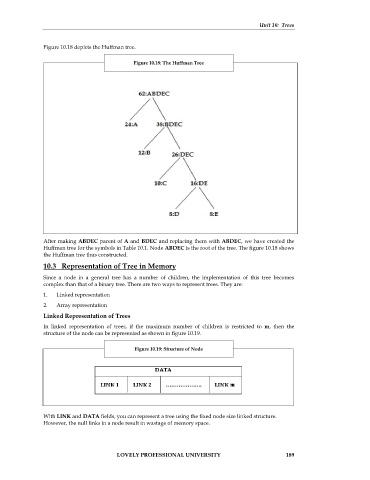
Figure 10.18 depicts the Huffman tree.
Figure 10.18: The Huffman Tree
After making ABDEC parent of A and BDEC and replacing them with ABDEC, we have created the
Huffman tree for the symbols in Table 10.1. Node ABDEC is the root of the tree. The figure 10.18 shows
the Huffman tree thus constructed.
10.3 Representation of Tree in Memory
Since a node in a general tree has a number of children, the implementation of this tree becomes
complex than that of a binary tree. There are two ways to represent trees. They are:
1. Linked representation
2. Array representation
Linked Representation of Trees
In linked representation of trees, if the maximum number of children is restricted to m, then the
structure of the node can be represented as shown in figure 10.19.
Figure 10.19: Structure of Node
With LINK and DATA fields, you can represent a tree using the fixed node size linked structure.
However, the null links in a node result in wastage of memory space.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 189