Page 211 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 211
Data Structure
11.2 Storage Representation of Binary Tree
The binary tree can be represented by dynamic allocation technique and sequential allocation technique.
In the dynamic allocation technique, memory is allocated to a node using a linked list and in the
sequential allocation technique, memory is allocated to a node using an array.
Linked Representation
The binary tree is structured mainly on three nodes -the root (parent) node, the left and the right child
nodes. In a linked representation, the nodes of the tree are indicated by three fields. They are:
1. info – It contains the actual information.
2. llink – It represents the address of the left sub-tree.
3. rlink – It represents the address of right sub-tree.
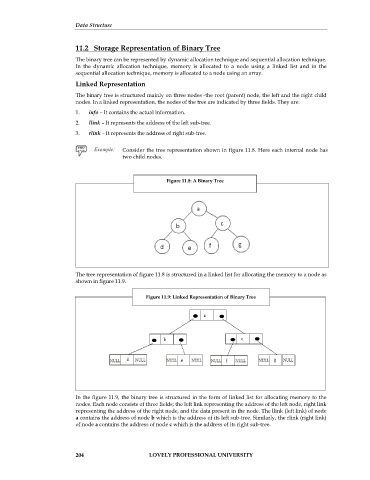
Consider the tree representation shown in figure 11.8. Here each internal node has
two child nodes.
Figure 11.8: A Binary Tree
The tree representation of figure 11.8 is structured in a linked list for allocating the memory to a node as
shown in figure 11.9.
Figure 11.9: Linked Representation of Binary Tree
In the figure 11.9, the binary tree is structured in the form of linked list for allocating memory to the
nodes. Each node consists of three fields; the left link representing the address of the left node, right link
representing the address of the right node, and the data present in the node. The llink (left link) of node
a contains the address of node b which is the address of its left sub-tree. Similarly, the rlink (right link)
of node a contains the address of node c which is the address of its right sub-tree.
204 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY