Page 182 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 182
Unit 12: Color and Shading Model
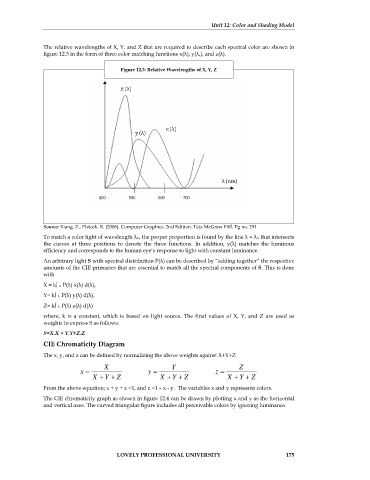
The relative wavelengths of X, Y, and Z that are required to describe each spectral color are shown in
figure 12.3 in the form of three color matching functions x(λ), y(λ,), and z(λ).
Figure 12.3: Relative Wavelengths of X, Y, Z
Source: Xiang. Z., Plstock. R. (2006). Computer Graphics. 2nd Edition. Tata McGraw Hill. Pg no. 291
To match a color light of wavelength λ0, the proper proportion is found by the line λ = λ0 that intersects
the curves at three positions to denote the three functions. In addition, y(λ) matches the luminous
efficiency and corresponds to the human eye’s response to light with constant luminance.
An arbitrary light S with spectral distribution P(λ) can be described by “adding together” the respective
amounts of the CIE primaries that are essential to match all the spectral components of S. This is done
with
X = k∫ λ P(λ) x(λ) d(λ),
Y= k∫ λ P(λ) y(λ) d(λ),
Z= k∫ λ P(λ) z(λ) d(λ)
where, k is a constant, which is based on light source. The final values of X, Y, and Z are used as
weights to express S as follows:
S=X.X + Y.Y+Z.Z
CIE Chromaticity Diagram
The x, y, and z can be defined by normalizing the above weights against X+Y+Z
X Y Z
x = y = z =
X + Y + Z X + Y + Z X + Y + Z
From the above equation; x + y + z =1, and z =1 – x - y. The variables x and y represents colors.
The CIE chromaticity graph as shown in figure 12.4 can be drawn by plotting x and y as the horizontal
and vertical axes. The curved triangular figure includes all perceivable colors by ignoring luminance.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 175