Page 46 - DCAP507_SYSTEM_SOFTWARE
P. 46
System Software
Notes output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling
peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
For large systems, the operating system has even greater responsibilities and powers. It is like
a traffic cop - it makes sure that different programs and users running at the same time do not
interfere with each other. The operating system is also responsible for security, ensuring that
unauthorized users do not access the system.
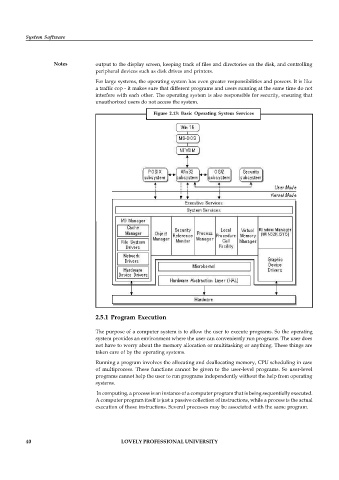
Figure 2.13: Basic Operating System Services
2.5.1 Program Execution
The purpose of a computer system is to allow the user to execute programs. So the operating
system provides an environment where the user can conveniently run programs. The user does
not have to worry about the memory allocation or multitasking or anything. These things are
taken care of by the operating systems.
Running a program involves the allocating and deallocating memory, CPU scheduling in case
of multiprocess. These functions cannot be given to the user-level programs. So user-level
programs cannot help the user to run programs independently without the help from operating
systems.
In computing, a process is an instance of a computer program that is being sequentially executed.
A computer program itself is just a passive collection of instructions, while a process is the actual
execution of those instructions. Several processes may be associated with the same program.
40 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY