Page 122 - DCAP606_BUSINESS_INTELLIGENCE
P. 122
Unit 8: Advanced Measures and Calculations
Instead, you probably want to know the sum of all profits divided by the sum of all sales. That Notes
formula is shown below:
Margin = SUM( [Profit]) / SUM([Sales])
In this case, the division is performed after each measure is aggregated. An aggregate calculation
allows you to create formulas like this.
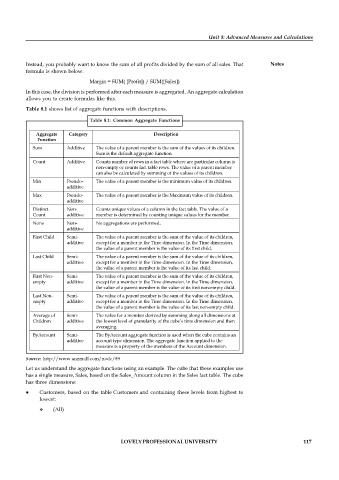
Table 8.1 shows list of aggregate functions with descriptions.
Table 8.1: Common Aggregate Functions
Aggregate Category Description
Function
Sum Additive The value of a parent member is the sum of the values of its children.
Sum is the default aggregate function.
Count Additive Counts number of rows in a fact table where are particular column is
non-empty or counts fact table rows. The value of a parent member
can also be calculated by summing of the values of its children.
Min Pseudo- The value of a parent member is the minimum value of its children.
additive
Max Pseudo- The value of a parent member is the Maximum value of its children.
additive
Distinct Non- Counts unique values of a column in the fact table. The value of a
Count additive member is determined by counting unique values for the member.
None Non- No aggregations are performed.
additive
First Child Semi- The value of a parent member is the sum of the value of its children,
additive except for a member in the Time dimension. In the Time dimension,
the value of a parent member is the value of its first child.
Last Child Semi- The value of a parent member is the sum of the value of its children,
additive except for a member in the Time dimension. In the Time dimension,
the value of a parent member is the value of its last child.
First Non- Semi- The value of a parent member is the sum of the value of its children,
empty additive except for a member in the Time dimension. In the Time dimension,
the value of a parent member is the value of its first non-empty child.
Last Non- Semi- The value of a parent member is the sum of the value of its children,
empty additive except for a member in the Time dimension. In the Time dimension,
the value of a parent member is the value of its last non-empty child.
Average of Semi- The value for a member derived by summing along all dimensions at
Children additive the lowest level of granularity of the cube’s time dimension and then
averaging.
ByAccount Semi- The ByAccount aggregate function is used when the cube contains an
additive account type dimension. The aggregate function applied to the
measure is a property of the members of the Account dimension.
Source: http://www.anzmall.com/node/89
Let us understand the aggregate functions using an example. The cube that these examples use
has a single measure, Sales, based on the Sales_Amount column in the Sales fact table. The cube
has three dimensions:
Customers, based on the table Customers and containing these levels from highest to
lowest:
(All)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 117