Page 35 - DCAP606_BUSINESS_INTELLIGENCE
P. 35
Business Intelligence
Notes Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. Dimensional model comprises of a .............................. and numerous dimensional tables
and is used for assessing summarized data.
2. .................................. define the axis of enquiry of a fact.
3.2 Facts Table
Fact table generally represent a process or reporting environment that is of value to the
organization. It is important to determine the identity of the fact table and specify exactly what
it represents. A fact table typically corresponds to an associative entity in the E-R model.
They must be listed in a logical fact table. Each measure has its own aggregation rules such as
ADD, AVG, MIN or MAX. Aggregation rules define the way by which business would like to
contrast standards of a measured value.
!
Caution Facts are the measurements associated with fact table records at fact table
granularity.
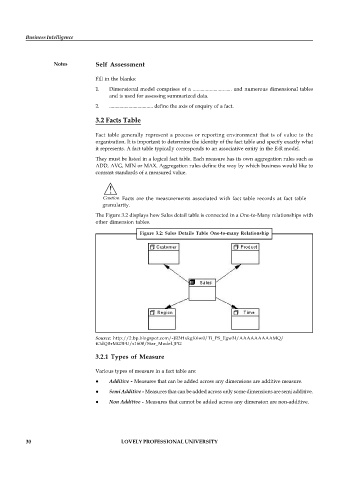
The Figure 3.2 displays how Sales detail table is connected in a One-to-Many relationships with
other dimension tables.
Figure 3.2: Sales Details Table One-to-many Relationship
Source: http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-JR3HxkgK6w0/Ti_PS_Egw3I/AAAAAAAAAMQ/
tOdQBrMG3FU/s1600/Star_Model.JPG
3.2.1 Types of Measure
Various types of measure in a fact table are:
Additive - Measures that can be added across any dimensions are additive measure.
Semi Additive - Measures that can be added across only some dimensions are semi additive.
Non Additive - Measures that cannot be added across any dimension are non-additive.
30 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY