Page 41 - DCAP606_BUSINESS_INTELLIGENCE
P. 41
Business Intelligence
Notes
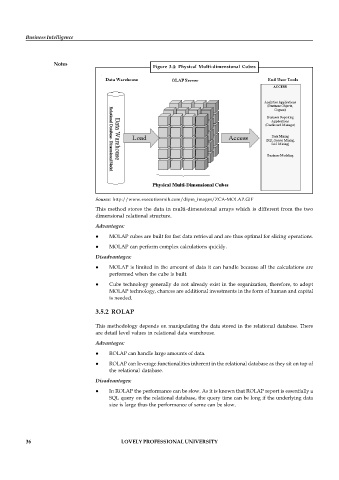
Figure 3.4: Physical Multi-dimensional Cubes
Source: http://www.executionmih.com/dipm_images/ZCA-MOLAP.GIF
This method stores the data in multi-dimensional arrays which is different from the two
dimensional relational structure.
Advantages:
MOLAP cubes are built for fast data retrieval and are thus optimal for slicing operations.
MOLAP can perform complex calculations quickly.
Disadvantages:
MOLAP is limited in the amount of data it can handle because all the calculations are
performed when the cube is built.
Cube technology generally do not already exist in the organization, therefore, to adopt
MOLAP technology, chances are additional investments in the form of human and capital
is needed.
3.5.2 ROLAP
This methodology depends on manipulating the data stored in the relational database. There
are detail level values in relational data warehouse.
Advantages:
ROLAP can handle large amounts of data.
ROLAP can leverage functionalities inherent in the relational database as they sit on top of
the relational database.
Disadvantages:
In ROLAP the performance can be slow. As it is known that ROLAP report is essentially a
SQL query on the relational database, the query time can be long if the underlying data
size is large thus the performance of same can be slow.
36 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY