Page 49 - DCAP606_BUSINESS_INTELLIGENCE
P. 49
Business Intelligence
Notes summarized into multidimensional views and hierarchies. By summarizing predicted queries
into multidimensional views prior to run time, OLAP tools provide the benefit of increased
performance over traditional database access tools. Most of the resource-intensive calculation
that is required to summarize the data is done before a query is submitted. This unit on OLAP
explains the concepts and advantages of OLAP, spreadsheet formulas. It also covers study of
metadata.
4.1 Basic Concepts of OLAP
OLAP is a database expertise that has been optimized for querying and describing, rather than
of processing transactions. OLAP data is drawn from historical data, and it is aggregated into
structures that allow complicated analysis. Data in OLAP is also coordinated hierarchically and
placed in cubes instead of tables. It is a sophisticated technology that benefits multidimensional
structures to supply fast access to data for analysis. This association makes it easy for a PivotTable
report or PivotChart report to show high-level abstracts, such as total sales across an entire
region, and also show the details for sites where sales are particularly strong.
OLAP databases contain two basic types of data: measures, which are numeric data, the quantities
and averages that you use to make informed enterprise decisions, and dimensions, which are
the categories that you use to coordinate with these measures. OLAP databases help to coordinate
data by many levels of details by utilizing the identical categories that you are familiar with to
analyse the data.
4.1.1 Components of OLAP
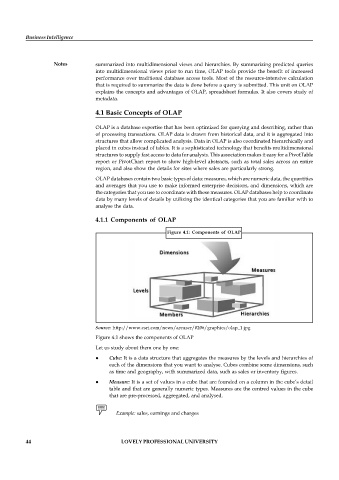
Figure 4.1: Components of OLAP
Source: http://www.esri.com/news/arcuser/0206/graphics/olap_1.jpg
Figure 4.1 shows the components of OLAP
Let us study about them one by one:
Cube: It is a data structure that aggregates the measures by the levels and hierarchies of
each of the dimensions that you want to analyse. Cubes combine some dimensions, such
as time and geography, with summarized data, such as sales or inventory figures.
Measure: It is a set of values in a cube that are founded on a column in the cube’s detail
table and that are generally numeric types. Measures are the centred values in the cube
that are pre-processed, aggregated, and analysed.
Example: sales, earnings and charges
44 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY