Page 62 - DCAP101_BASIC_COMPUTER_SKILLS
P. 62
Unit 4: Secondary Storage Devices
Notes
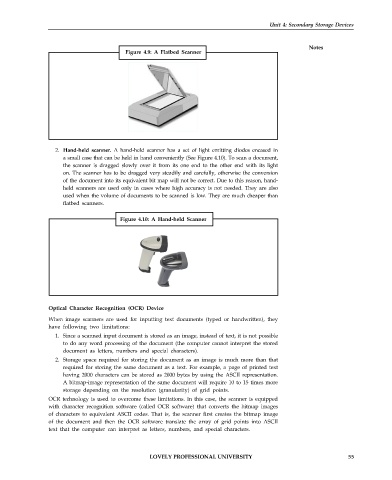
Figure 4.9: A Flatbed Scanner
2. Hand-held scanner. A hand-held scanner has a set of light emitting diodes encased in
a small case that can be held in hand conveniently (See Figure 4.10). To scan a document,
the scanner is dragged slowly over it from its one end to the other end with its light
on. The scanner has to be dragged very steadily and carefully, otherwise the conversion
of the document into its equivalent bit map will not be correct. Due to this reason, hand-
held scanners are used only in cases where high accuracy is not needed. They are also
used when the volume of documents to be scanned is low. They are much cheaper than
flatbed scanners.
Figure 4.10: A Hand-held Scanner
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Device
When image scanners are used for inputting text documents (typed or handwritten), they
have following two limitations:
1. Since a scanned input document is stored as an image, instead of text, it is not possible
to do any word processing of the document (the computer cannot interpret the stored
document as letters, numbers and special characters).
2. Storage space required for storing the document as an image is much more than that
required for storing the same document as a text. For example, a page of printed text
having 2000 characters can be stored as 2000 bytes by using the ASCII representation.
A bitmap-image representation of the same document will require 10 to 15 times more
storage depending on the resolution (granularity) of grid points.
OCR technology is used to overcome these limitations. In this case, the scanner is equipped
with character recognition software (called OCR software) that converts the bitmap images
of characters to equivalent ASCII codes. That is, the scanner first creates the bitmap image
of the document and then the OCR software translate the array of grid points into ASCII
text that the computer can interpret as letters, numbers, and special characters.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 55