Page 60 - DMGT102_MERCANTILE_LAWS_I
P. 60
Mercantile Laws-I
Notes Differences between Fraud and Misrepresentation
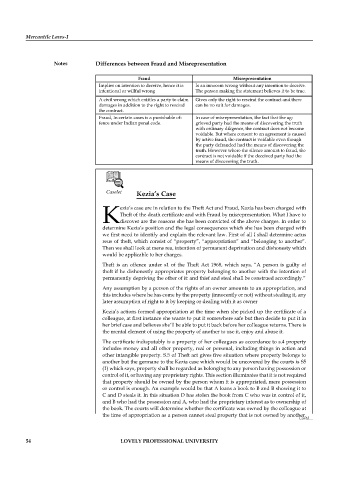
Fraud Misrepresentation
Implies on intention to deceive, hence it is Is an innocent wrong without any intention to deceive.
intentional or willful wrong The person making the statement believes it to be true.
A civil wrong which entitles a party to claim Gives only the right to rescind the contract and there
damages in addition to the right to rescind can be no suit for damages.
the contract.
Fraud, In certain cases is a punishable of- In case of misrepresentation, the fact that the ag-
fence under Indian penal code. grieved party had the means of discovering the truth
with ordinary diligence, the contract does not become
voidable. But where consent to an agreement is caused
by active fraud, the contract is voidable even though
the party defrauded had the means of discovering the
truth. However where the silence amount to fraud, the
contract is not voidable if the deceived party had the
means of discovering the truth.
Caselet Kezia’s Case
ezia’s case are in relation to the Theft Act and Fraud, Kazia has been charged with
Theft of the death certificate and with Fraud by misrepresentation. What I have to
Kdiscover are the reasons she has been convicted of the above charges. In order to
determine Kezia’s position and the legal consequences which she has been charged with
we first need to identify and explain the relevant law. First of all I shall determine actus
reus of theft, which consist of “property”, “appropriation” and “belonging to another”.
Then we shall look at mens rea, intention of permanent deprivation and dishonesty which
would be applicable to her charges.
Theft is an offence under s1 of the Theft Act 1968, which says, “A person is guilty of
theft if he dishonestly appropriates property belonging to another with the intention of
permanently depriving the other of it: and thief and steal shall be construed accordingly.”
Any assumption by a person of the rights of an owner amounts to an appropriation, and
this includes where he has come by the property (innocently or not) without stealing it, any
later assumption of right to it by keeping or dealing with it as owner
Kezia’s actions formed appropriation at the time when she picked up the certificate of a
colleague, at first instance she wants to put it somewhere safe but then decide to put it in
her brief case and believes she’ll be able to put it back before her colleague returns. There is
the mental element of using the property of another to use it, enjoy and abuse it.
The certificate indisputably is a property of her colleagues as accordance to s.4 property
includes money and all other property, real or personal, including things in action and
other intangible property. S.5 of Theft act gives five situation where property belongs to
another but the germane to the Kezia case which would be uncovered by the courts is S5
(1) which says, property shall be regarded as belonging to any person having possession or
control of it, or having any proprietary rights. This section illuminates that it is not required
that property should be owned by the person whom it is appropriated, mere possession
or control is enough. An example would be that A loans a book to B and B showing it to
C and D steals it. In this situation D has stolen the book from C who was in control of it,
and B who had the possession and A, who had the proprietary interest as to ownership of
the book. The courts will determine whether the certificate was owned by the colleague at
the time of appropriation as a person cannot steal property that is not owned by another.
Contd....
54 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY