Page 94 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 94
Unit 7: Production Theory
7.2.1 Short Run and Long Run Production Function Notes
The above features show that some quantity of both the inputs is required to produce a given
quantity of output. A two input long run production function for quantities of labour and capital
upto 10 units can be expressed as in Table 7.1.
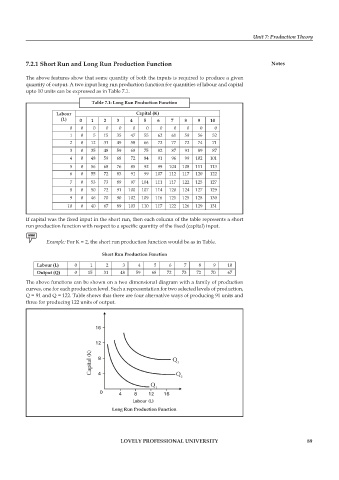
Table 7.1: Long Run Production Function
Labour Capital (K)
(L) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 5 15 35 47 55 62 61 59 56 52
2 0 12 31 49 58 66 72 77 72 74 71
3 0 35 48 59 68 75 82 87 91 89 87
4 0 48 59 68 72 84 91 96 99 102 101
5 0 56 68 76 85 92 99 104 108 111 113
6 0 55 72 83 91 99 107 112 117 120 122
7 0 53 73 89 97 104 111 117 122 125 127
8 0 50 72 91 100 107 114 120 124 127 129
9 0 46 70 90 102 109 116 121 125 128 130
10 0 40 67 89 103 110 117 122 126 129 131
If capital was the fixed input in the short run, then each column of the table represents a short
run production function with respect to a specific quantity of the fixed (capital) input.
Example: For K = 2, the short run production function would be as in Table.
Short Run Production Function
Labour (L) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Output (Q) 0 15 31 48 59 68 72 73 72 70 67
The above functions can be shown on a two dimensional diagram with a family of production
curves, one for each production level. Such a representation for two selected levels of production,
Q = 91 and Q = 122. Table shows that there are four alternative ways of producing 91 units and
three for producing 122 units of output.
Long Run Production Function
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 89