Page 72 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 72
Unit 4: Presentation of Data
The construction of a frequency curve should be done very carefully by avoiding, as far as Notes
possible, the sharp and sudden turns. Smoothing should be done so that the area under the
curve is approximately equal to the area under the histogram.
A frequency curve can be used for estimating the rate of increase or decrease of the
frequency at a given point. It can also be used to determine the frequency of a value (or of
values in an interval) of the variable. This method of determining frequencies is popularly
known as interpolation method.
14. Cumulative Frequency Curve or Ogive: The curve obtained by representing a cumulative
frequency distribution on a graph is known as cumulative frequency curve or ogive. Since
a cumulative frequency distribution can of ‘less than’ or ‘greater than’ type and, accordingly,
there are two type of ogive, ‘less than ogive’ and ‘more than ogive’.
An ogive is used to determine certain positional averages like median, quartiles, deciles,
percentiles, etc. We can also determine the percentage of cases lying between certain
limits. Various frequency distributions can be compared on the basis of their ogives.
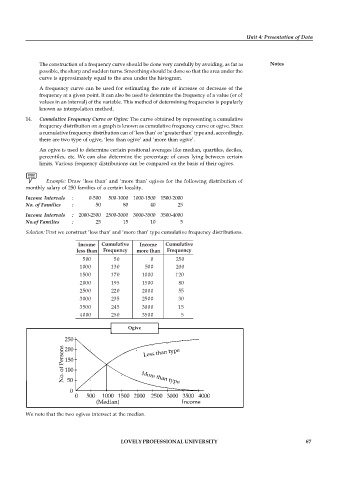
Example: Draw ‘less than’ and ‘more than’ ogives for the following distribution of
monthly salary of 250 families of a certain locality.
Income Intervals : 0-500 500-1000 1000-1500 1500-2000
No. of Families : 50 80 40 25
Income Intervals : 2000-2500 2500-3000 3000-3500 3500-4000
No.of Families : 25 15 10 5
Solution: First we construct ‘less than’ and ‘more than’ type cumulative frequency distributions.
Income Cumulative Income Cumulative
less than Frequency more than Frequency
500 50 0 250
1000 130 500 200
1500 170 1000 120
2000 195 1500 80
2500 220 2000 55
3000 235 2500 30
3500 245 3000 15
4000 250 3500 5
Ogive
We note that the two ogives intersect at the median.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 67