Page 193 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 193
Macro Economics
Notes 7. In India, monetary policy measures to control inflation are taken by..............................
(a) SEBI (b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) State Bank of India (d) Finance Ministry
8. Which of these is a measure to deal with cost-push inflation?
(a) Selective credit control (b) Tax control
(c) Controlling public expenditure (d) Wage rate control
9. Price control will lead to increase in quantity demanded and decrease in quantity supplied
because the fixed price has to be .................................... the market equilibrium price.
(a) Above (b) Below
(c) At par with (d) More or equal to
11.3 Philips Curve
Single wage costs form a prime component of the price structure. Economists attempting to
study supply inflation have recently focussed attention on the relationship between the rate of
wage rise (rate of inflation) and the rate of unemployment in the economy. This analysis runs in
terms of the “Phillips curve” (named after AW Phillips, a British economist, who attempted an
empirical explanation of inflation).
Did u know? Phillips found negative relation between the rate of wage increases and the
rate of unemployment in England during the period 1862-1957.
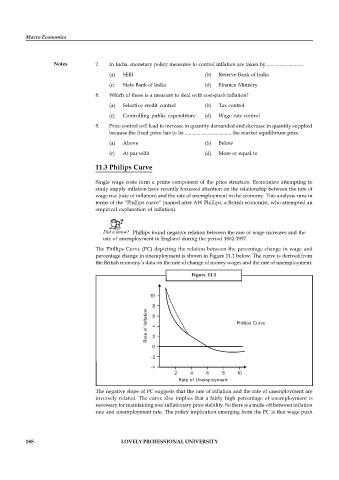
The Phillips Curve (PC) depicting the relation between the percentage change in wage and
percentage change in unemployment is shown in Figure 11.1 below. The curve is derived from
the British economy’s data on the rate of change of money wages and the rate of unemployment.
Figure 11.1
The negative slope of PC suggests that the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment are
inversely related. The curve also implies that a fairly high percentage of unemployment is
necessary for maintaining non-inflationary price stability. So there is a trade-off between inflation
rate and unemployment rate. The policy implication emerging from the PC is that wage push
188 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY