Page 22 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 22
Unit 2: National Income
Notes
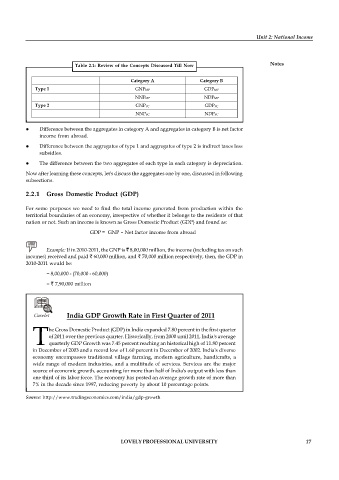
Table 2.1: Review of the Concepts Discussed Till Now
Category A Category B
Type 1 GNPMP GDPMP
NNPMP NDPMP
Type 2 GNPFC GDPFC
NNPFC NDPFC
Difference between the aggregates in category A and aggregates in category B is net factor
income from abroad.
Difference between the aggregates of type 1 and aggregates of type 2 is indirect taxes less
subsidies.
The difference between the two aggregates of each type in each category is depreciation.
Now after learning these concepts, let's discuss the aggregates one by one, discussed in following
subsections.
2.2.1 Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
For some purposes we need to find the total income generated from production within the
territorial boundaries of an economy, irrespective of whether it belongs to the residents of that
nation or not. Such an income is known as Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and found as:
GDP = GNP – Net factor income from abroad
Example: If in 2010-2011, the GNP is 8,00,000 million, the income (including tax on such
incomes) received and paid 60,000 million, and 70,000 million respectively, then, the GDP in
2010-2011 would be:
= 8,00,000 - (70,000 - 60,000)
= 7,90,000 million
Caselet India GDP Growth Rate in First Quarter of 2011
he Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in India expanded 7.80 percent in the first quarter
of 2011 over the previous quarter. Historically, from 2000 until 2011, India's average
Tquarterly GDP Growth was 7.45 percent reaching an historical high of 11.80 percent
in December of 2003 and a record low of 1.60 percent in December of 2002. India's diverse
economy encompasses traditional village farming, modern agriculture, handicrafts, a
wide range of modern industries, and a multitude of services. Services are the major
source of economic growth, accounting for more than half of India's output with less than
one third of its labor force. The economy has posted an average growth rate of more than
7% in the decade since 1997, reducing poverty by about 10 percentage points.
Source: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/india/gdp-growth
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 17