Page 48 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 48
Unit 3: Theories of Income, Output and Employment: Classical Theory
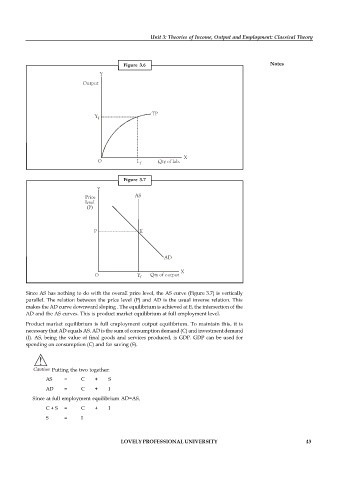
Figure 3.6 Notes
Y
Output
TP
Y f
X
O L f Qty of lab.
Figure 3.7
Y
Price AS
level
(P)
P E
AD
X
O Y f Qty of output
Since AS has nothing to do with the overall price level, the AS curve (Figure 3.7) is vertically
parallel. The relation between the price level (P) and AD is the usual inverse relation. This
makes the AD curve downward sloping . The equilibrium is achieved at E, the intersection of the
AD and the AS curves. This is product market equilibrium at full employment level.
Product market equilibrium is full employment output equilibrium. To maintain this, it is
necessary that AD equals AS. AD is the sum of consumption demand (C) and investment demand
(I). AS, being the value of final goods and services produced, is GDP. GDP can be used for
spending on consumption (C) and for saving (S).
!
Caution Putting the two together:
AS = C + S
AD = C + I
Since at full employment equilibrium AD=AS,
C + S = C + I
S = I
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 43