Page 54 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 54
Unit 3: Theories of Income, Output and Employment: Classical Theory
3.2.4 Simultaneous Equilibrium in all the Markets Notes
The basic features of the classical model of full employment are that (a) all the markets are
interlinked and change in one market brings changes in other markets and (b) all the markets
are simultaneously in equilibrium. This makes the classical model a general equilibrium model.
The three markets are simultaneously in equilibrium in the following manner:
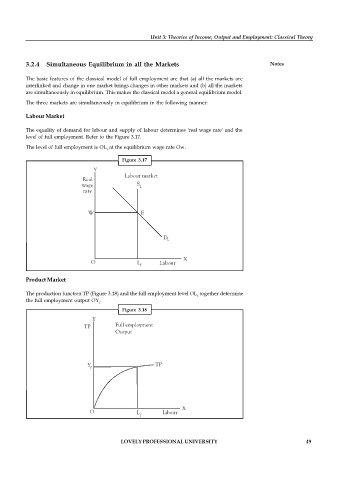
Labour Market
The equality of demand for labour and supply of labour determines 'real wage rate' and the
level of full employment. Refer to the Figure 3.17.
The level of full employment is OL at the equilibrium wage rate Ow.
f
Figure 3.17
Y
Labour market
Real
wage S L
rate
W E
D L
X
O L Labour
f
Fig. 10.16
Product Market
The production function TP (Figure 3.18) and the full employment level OL together determine
f
the full employment output OY .
f
Figure 3.18
Y
TP Full employment
Output
Y TP
f
X
O L labour
f
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 49